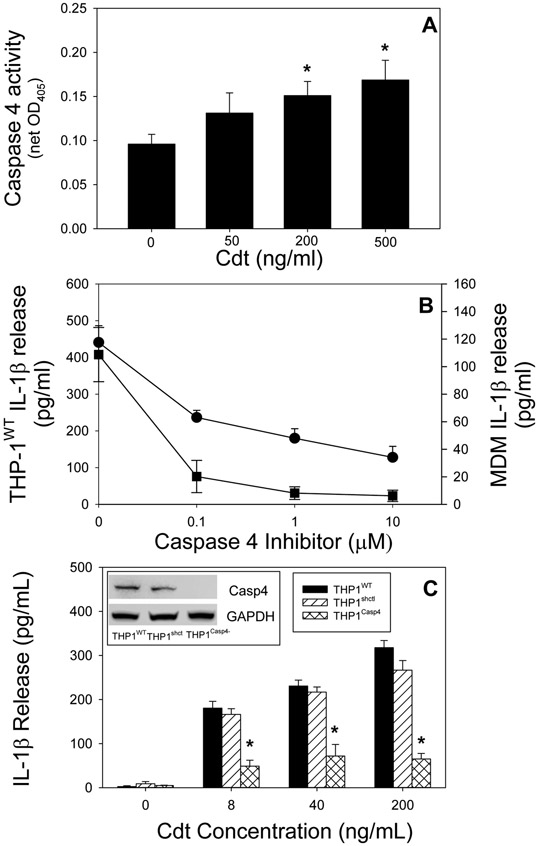
Fig. 1.
Cdt-induced release of IL-1β is dependent upon caspase-4 activation. Panel A: THP-1WT-derived macrophages were treated with Cdt and analyzed for caspase-4 activation. Results are plotted as Cdt concentration vs caspase-4 activity (net OD405) and are the mean±SEM of four experiments. Panel B: THP-1WT- (circle) and monocyte (square)-derived macrophages were pre-treated with varying amounts of the caspase-4 inhibitor LEVD-CHO followed by the addition of 200 ng/ml Cdt. Supernatants were harvested 5 hrs later and analyzed for IL-1β by ELISA. Results are plotted as mean±SEM pg/ml IL-1β vs caspase-4 inhibitor concentration. Results are the mean of 3 experiments; note: samples receiving caspase-4 inhibitor were significantly lower at all concentrations than samples receiving Cdt alone (p<0.05). Panel C: Macrophages derived from THP-1WT (solid bar), THP-1shctrl (hatched bars) and THP-1Casp4− (cross-hatched bars) were treated with varying concentrations of Cdt for 5 hrs. Supernatants were harvested and analyzed by ELISA for IL-1β. Results are plotted as the mean±SEM pg/ml IL-1β for four experiments versus Cdt concentration. Inset shows caspase-4 protein levels (Western blot) in cell extracts obtained from THP-1WT , THP-1shctrl and THP-1CasP4− derived macrophages, *indicates statistical significance (p<0.05 relative to THP-1WT-derived macrophages treated with the same concentration of Cdt.