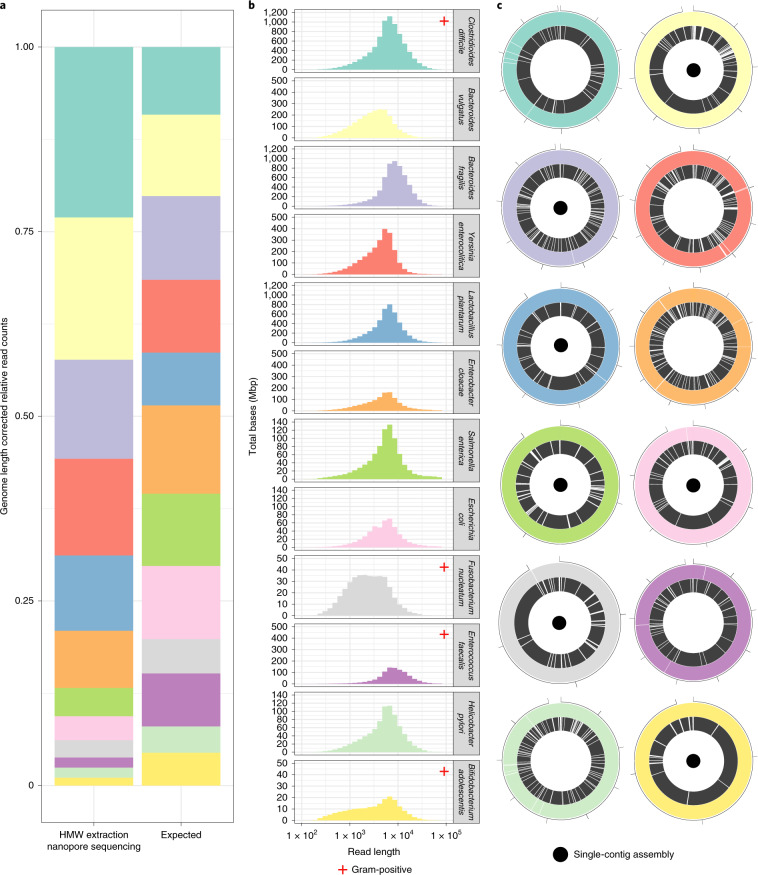
Fig. 1. Taxonomic read composition, per-organism read-length distributions and genome assemblies in a defined 12-species bacterial mixture.
a, Relative read counts are shown for the expected equal composition of bacterial cells and the observed composition, with correction for relative genome size. b, Read-length distributions per organism. Individual organisms demonstrate varying read-length distributions in some cases. c, Circos plots demonstrate the relative assembly contiguity of the nanopore versus short-read assembly approaches. Nanopore sequencing and assembly (colored outer ring) outperforms short-read assembly (black inner ring), producing complete genome assemblies (small black inner dots) in seven of 12 cases, with a further three assembled in four contigs or fewer. Numbers indicate genome size in megabases. Note that complete assemblies may contain one apparent break due to differing linearization breakpoints in reference and assembly sequences.