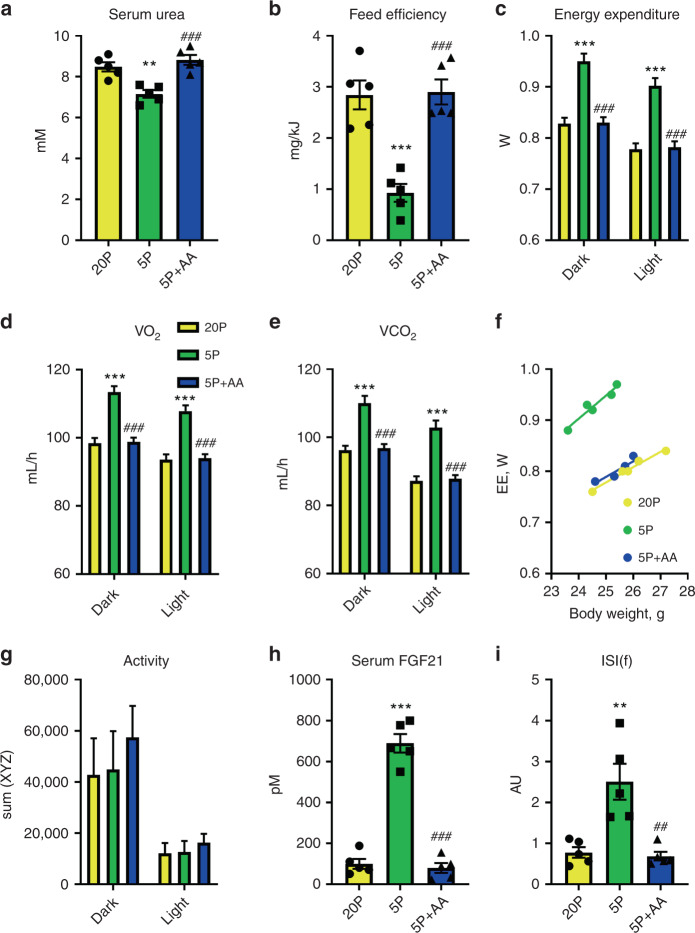
Fig. 1. Dietary amino acids are required for the systemic metabolic effects of dietary protein dilution.
a Serum urea levels of mice in response to a 3-week treatment with diets containing 20% energy from protein (20P), 5% energy from protein (5P), and 5% energy from protein and 15% energy from amino acids to match that of 20P. Data are mean and SEM; n = 5 individual mice per group. Data were analysed by one-way ANOVA with Holm–Sidak post-hoc tests. Different than 20P: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Different than 5P: #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001. b Feed efficiency of mice as in (a). c Energy expenditure over the different day phases of mice as in (a). d The rate of O2 consumption (VO2) over the different day phases of mice as in (a). e The rate of CO2 production (VCO2) over the different day phases of mice as in (a). f Scatter plot of energy expenditure (EE) versus body weight of mice as in (a). g Physical activity as assessed by laser beam breaks across three physical dimensions (sumXYZ) over the different day phases of mice as in (a). h Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) levels of mice as in (a). i Insulin sensitivity index during fasting (ISI(f)) of mice as in (a).