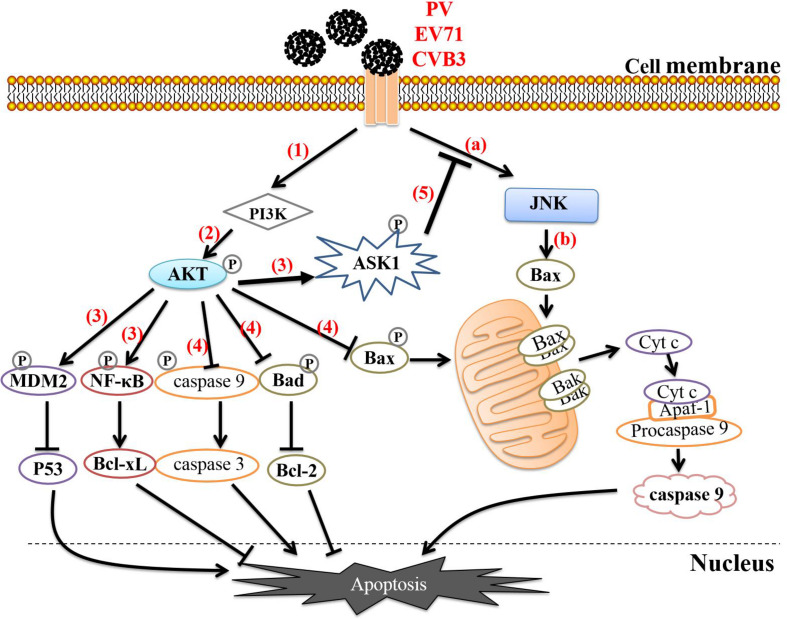
FIGURE 2.
Enteroviruses regulate apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT pathway. (a) Enteroviruses interact with cellular receptors to induce JNK phosphorylation. (b) Activated JNK activates Bax-dependent apoptosis. (1) Enteroviruses interact with cell receptors to activate the PI3K/AKT pathway. (2) PI3K activates Akt by phosphorylating threonine (Thr) 308 and serine (Ser) 473 on Akt. (3) Activated Akt phosphorylates NF-κB, MDM2, and ASK1. Phosphorylation of NF-κB activates its transcription function, allowing it to enhance the expression of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-xl. Phosphorylated MDM2 can inactivate or degrade P53, thereby blocking the P53-mediated proapoptotic transcription reaction. (4) Activated Akt directly phosphorylates Bad, Bax, and caspase 9, causing them to lose their ability to promote apoptosis and thereby effectively blocking apoptosis. (5) ASK1 is the upstream regulatory factor of JNK, and phosphorylated ASK1 negatively regulates the activation of JNK, thereby delaying activation of the proapoptotic protein Bax and effectively inhibiting apoptosis.