FIG 10.
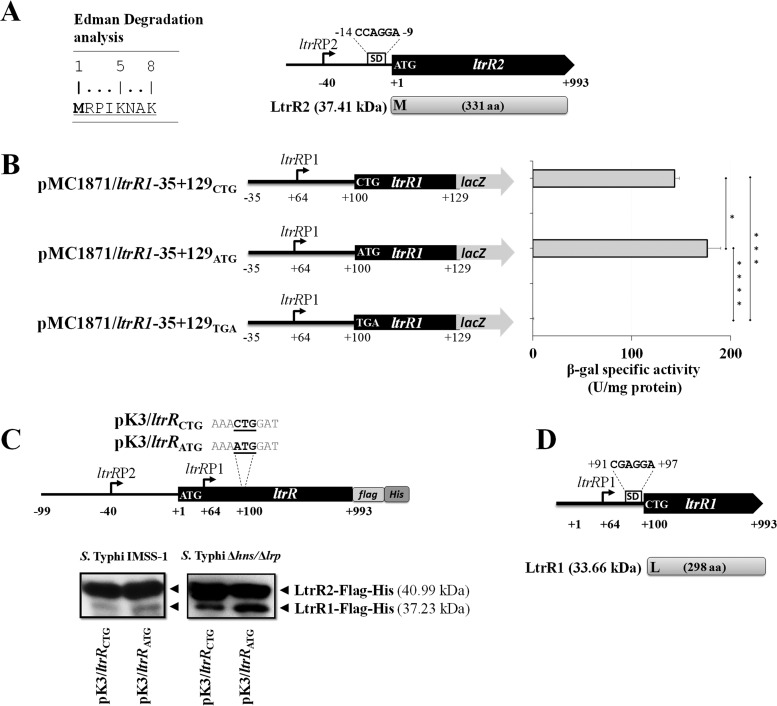
LtrR2 and LtrR1 translational start site determination. (A) Edman degradation analysis showing the N-terminal sequence (8 amino acids) of LtrR2. M (methionine) corresponds to the LtrR2 translational start codon. Shown is a schematic representation of ltrR2 showing its transcriptional start site ltrRP2; a putative Shine-Dalgarno sequence, CCAGGA, located 9 bp upstream of the LtrR2 translational start codon ATG; and the corresponding protein of 37.41 kDa. (B) Translational lacZ fusions pMC1871/ltrR1-35+129CTG, pMC1871/ltrR1-35+129ATG, and pMC1871/ltrR1-35+129TGA containing the CTG wild-type initiation codon as well as an ATG or a TGA substitution. The β-galactosidase specific activity was evaluated in the S. Typhi IMSS-1 strain at an OD595 of 1.0 in N-MM. The values are the means ± standard deviations from two independent experiments performed in duplicate (n = 4). Statistically different values are indicated (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001). (C) Western blotting was performed with 25 μg of purified proteins from S. Typhi IMSS-1 or S. Typhi Δhns Δlrp containing pK3/ltrRCTG or pK3/ltrRATG that expresses LtrR2-Flag-His (40.99 kDa), LtrR1CTG-Flag-His (37.23 kDa), or LtrR1ATG-Flag-His (37.24 kDa). (D) Genetic representation of the ltrR1 gene showing its transcriptional start site ltrRP1 (residue +64); a putative Shine-Dalgarno sequence, +91CGAGGA+97; and the corresponding LtrR1 protein of 33.66 kDa with its leucine translational start site (L).