Fig. 4.
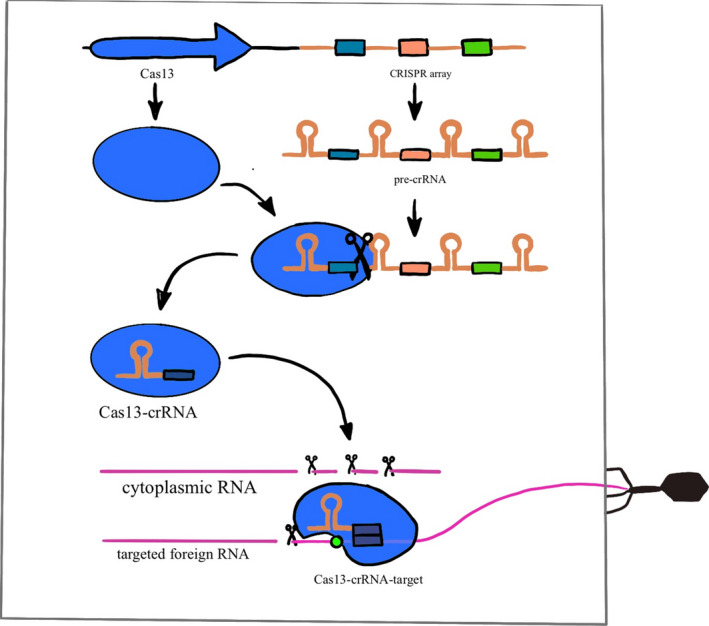
The top of the drawing represents the DNA encoding for the Cas 13 protein and the CRISPR array, which contains the targets for Cas13 cleavage and subsequent degradation. This array is transcribed into pre‐crRNA. The Cas13 protein turns this transcript into mature crRNAs, forming a crRNA‐Cas13 complex that in turns searches along existing RNA transcripts for matching sequences known as protospacers. Once this complementary protospacer is found, Cas13 undergoes a conformational change to enhance binding and activates the RNA cleavage activity of Cas13, which can then be used to degrade foreign viral RNA entering the cell as shown on the right side of the image. Adapted from [156].
