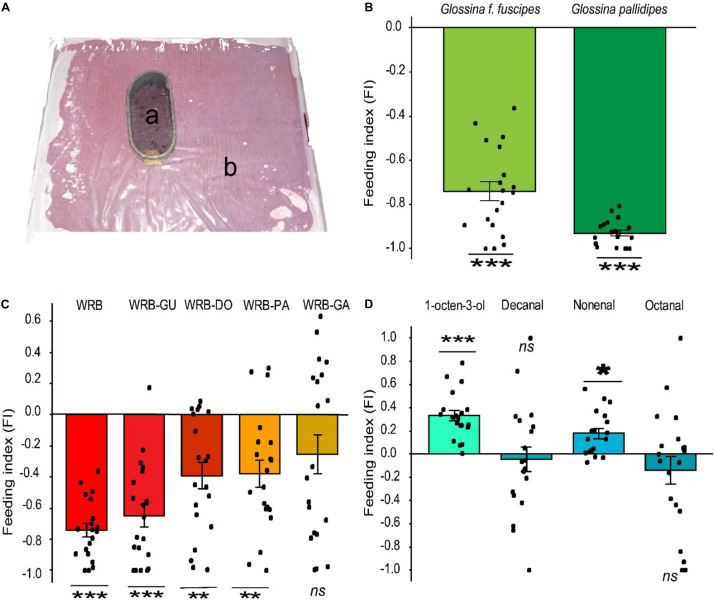
FIGURE 1.
Antifeeding effect of WRB. (A) Antifeeding bioassay setup: a represents the feeding cage, single fly/cage (original photo); b indicates the feeding tray containing sterile blood covered by a silicone membrane. (B) Feeding index (FI) of G. f. fuscipes and G. pallidipes fed on membrane treated with WRB. WRB, waterbuck repellent blend. Deviation of the feeding index from zero was tested with a Student’s t-test (P < 0.05). (C) Feeding index (FI) of G. f. fuscipes fed on membrane treated with WRB and showing the contribution of each compound to the antifeeding effect. WRB-DO, WRB minus δ-octalactone; WRB-GA, WRB minus geranyl acetone; WRB-GU, WRB minus guaiacol; WRB-PA, WRB minus pentanoic acid. (D) Feeding index (FI) of G. f. fuscipes fed on membrane treated with positive controls (an attractant). Deviation of the feeding index from zero was tested with a Student’s t-test (P < 0.05). Level of significance: ***P < 0.0001; **P < 0.001; *P < 0.05, d represents the effect of size (Cohen’s d) and ns means not significant. Error bars represent standard error, n = 20 for each test. The graphs and the statistics were generated using R software (R Core Team, 2018), (version 3.5.1), www.R-project.org.