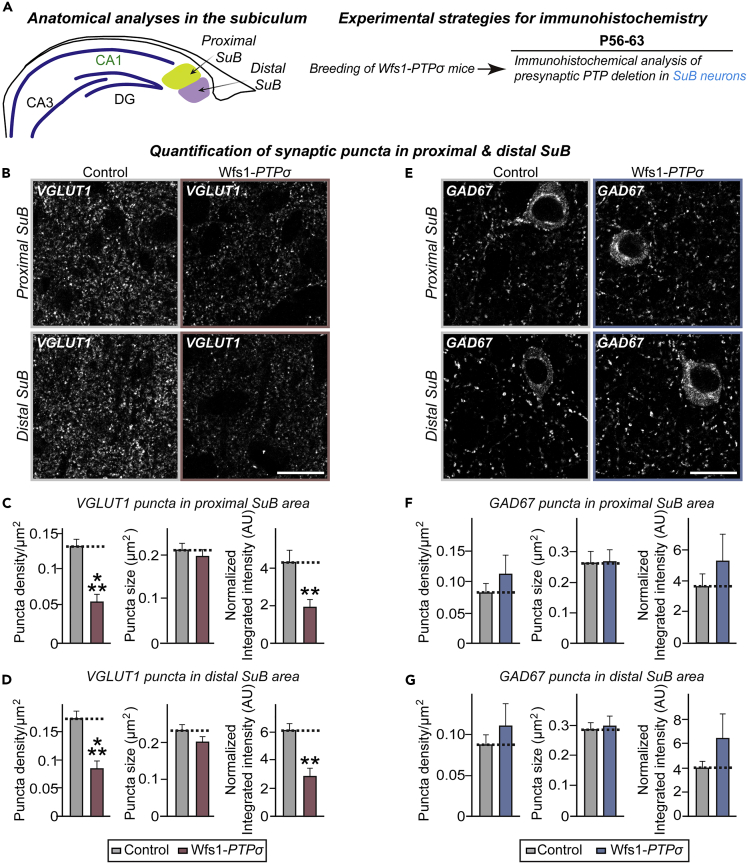
Figure 4.
Wfs1-PTPσ KO Mice Exhibit Decreased Excitatory Synaptic Innervation in Postsynaptic Subicular Pyramidal Neurons
(A) Schematic depiction of anatomical analyses in the subiculum. Each subiculum was divided into the proximal and distal subiculum.
(B and E) Representative immunofluorescence images of the proximal and distal SuB of Control and Wfs1-PTPσ mice using VGLUT1 (B) or GAD67 (E). Scale bar: 20 μm.
(C and F) Quantification of the density, size, and integrated intensity of VGLUT1-positive (C) and GAD67-positive (F) synaptic puncta in the proximal SuB. Data are means ± SEMs (n denotes the number of analyzed brain mice; 8 mice per group; ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001; Mann-Whitney U test).
(D and G) Quantification of the density, size, and integrated intensity of VGLUT1-positive (D) and GAD67-positive (G) synaptic puncta in the distal SuB. Data are means ± SEMs (n denotes the number of analyzed mice; 8 mice per group; ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; Mann-Whitney U test). See also Figures S7 and S8.