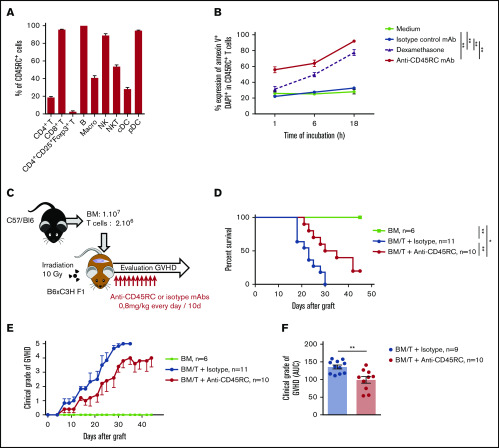
Figure 3.
Anti-mouse CD45RC mAb treatment alone delays GVHD following BM and T-cell administration. (A) Percentages of CD45RC+ cells among mouse splenocytes. Cells were first gated on morphology, doublet cells, and live cells. Mean expression of CD45RC ± SEM on different cell types (n = 3). (B) Mouse splenocytes incubated with anti-CD45RC or isotype control mAbs or dexamethasone as a positive control were stained with annexin V to analyze apoptosis. Results show the percentage expression of annexin V+ DAPI+ cells among CD45RC+ T cells for 1 to 18 hours compared with controls. **P < .01. (C) T cells were injected into irradiated mice at time of BM transfer (BM group n = 4). Mice were treated with anti-CD45RC (n = 11) or isotype control (n = 11) mAbs. Experiments were performed twice and data were pooled. Survival (D) and GVHD clinical score (E) were analyzed every day. *P < .05; **P < .01. (F) Histogram shows area under curve (AUC) of clinical GVHD. AUC was calculated for each mouse, and then an ANOVA test with post hoc analysis was performed. **P < .01.