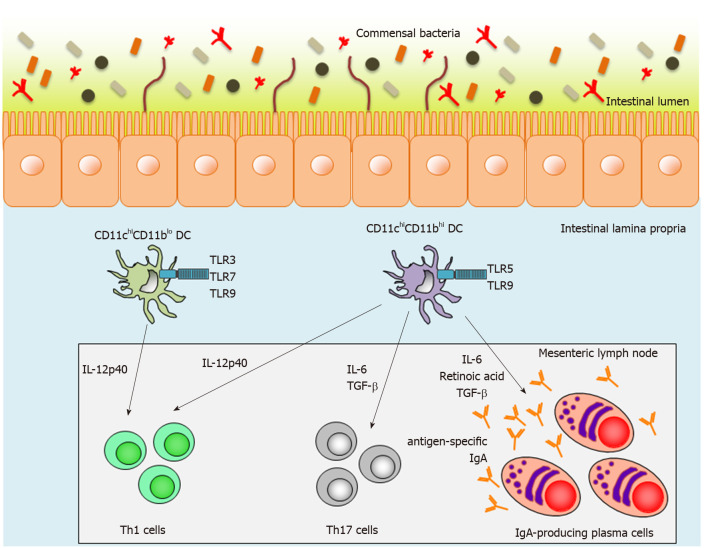
Figure 1.
Function of two distinct lamina propria dendritic cells in the small intestine. Mouse small-intestinal lamina propria dendritic cells (LPDCs) are divided into two subsets on the basis of CD11c and CD11b expression. CD11chiCD11blo LPDCs express Toll-like receptor (TLR) 3, TLR7 and TLR9, whereas CD11chiCD11bhi LPDCs express TLR5 and TLR9. After TLR stimulation, activated CD11chiCD11bhi LPDCs can produce interleukin (IL)-12p40, IL-6, transforming growth factor-β and retinoic acid, and subsequently induce antigen-specific Th1 and Th17 responses and antigen-specific-IgA-producing plasma cells. In contrast to CD11chiCD11bhi LPDCs, activated CD11chiCD11blo LPDCs can induce antigen-specific Th1 responses, but not antigen-specific Th17 responses and antigen-specific-IgA-producing plasma cells. TLR: Toll-like receptor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; IL: Interleukin; DC: Dendritic cell.