Figure 6.
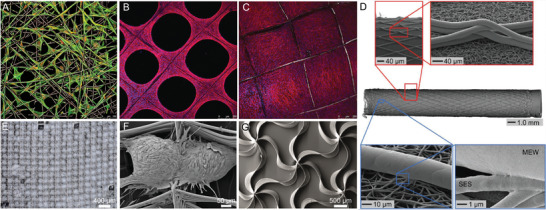
Examples of MEW products and integration within biofabrication. A) Top‐seeded human dermal fibroblasts on a MEW scaffold with a 30˚ pitch deposition. Osteoprogenitor cell line seeded on a 98% porous scaffold after B) six and C) 14 days in vitro, demonstrating typical pore closure for ECM depositing and proliferating cells. D) A multiphasic tube combining a solution electrospun substrate (SES) that is subsequently MEW at a specific angle. E) An adipose‐derived spheroid sheet for transfer, including F) SEM image of two spheroids in adjacent pores. G) sinusoidally printing and intersecting patterns for highly flexible scaffolds or soft network composites. (A) reproduced with permission.[ 91 ] Copyright 2013, IOP Publishing. (B,C) reproduced with permission.[ 92 ] Copyright 2015, Mary‐Anne Liebert. (D) reproduced with permission.[ 21 ] Copyright 2019, The Authors. Published by Wiley. (E,F) reproduced with permission.[ 81 ] Copyright 2019, The Authors, Published by WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (G) reproduced with permission.[ 55 ] Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
