Figure 4.
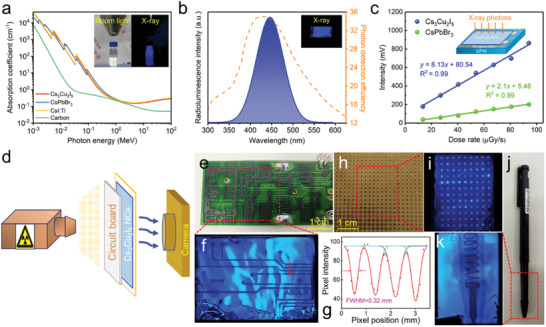
a) The X‐ray absorption coefficients of Cs3Cu2I5, CsPbBr3, CsI:Tl and carbon dots as a function of photon energy. The inset shows the photographs of colloidal solution of Cs3Cu2I5 NCs under room light and X‐ray irradiation with the energy of 50 keV. b) The RL spectrum of NCs film under 50 keV X‐ray excitation and the curve of photon detection efficiency of SiPM. The inset shows the photograph of the Cs3Cu2I5 film under X‐ray. c) The response intensity of Cs3Cu2I5 NCs and CsPbBr3 NCs as a function of X‐ray dose rate. The inset schematically shows the measurement, in which the NC films on glass are coupled with SiPM. d) Schematic of the prototype projection system for X‐ray imaging, and the sequence is an X‐ray source, a circuit board, Cs3Cu2I5 NC scintillators and a smartphone camera. e) The photograph and f) the corresponding X‐ray image of a circuit board. g) Point spread function (red arrow in (f)) of the intensity profile is fitted with Gaussian function, and the FWHM is obtained as the spatial resolution. h) The photograph and i) X‐ray image of a universal board. j) The photograph and k) X‐ray image of a ball‐point pen with an encapsulated metallic spring.
