Figure 3.
Single-Cell and Bulk Transcriptome Profiling of Microtissues
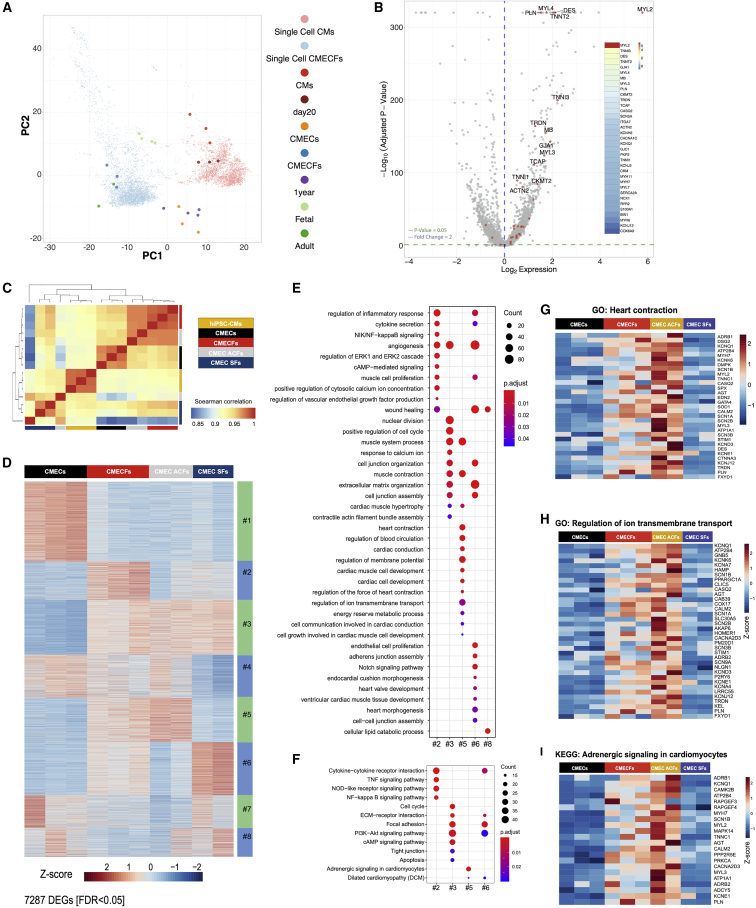
(A) PC analysis of single-cell (sc) and bulk RNA-seq of hiPSC-CMs at day 20 (single cell CMs; CMs), bulk CMECs (CMECs), and sc and bulk CMECFs (single cell CMECFs; CMECFs) from this study, with bulk hPSC-CMs (day 20), bulk primary human fetal heart (fetal), bulk hPSC-CMs (1 year), and primary human adult heart (adult) from RNA-seq in Kuppusamy et al. (2015); CM cluster). Colors represent different samples.
(B) Volcano plot and heatmaps displaying sorted log2 fold-change (FC) and adjusted p values showing expression of selected genes for hiPSC-CMs and CMECFs based on their scRNA-seq profiles. Log2FC > 0 indicates upregulated genes in the CM cluster of CMECFs versus hiPSC-CMs, whereas log2FC < 0 indicates upregulated genes in the CM cluster of hiPSC-CMs versus CMECFs.
(C) Spearman’s correlation heatmap of hiPSC-CMs, CMECs, CMECFs, CMEC ACFs, and CMEC SFs based on bulk RNA-seq.
(D) Heatmap showing gene expression in eight gene clusters from the consensus matrix across CMECs, CMECFs, CMEC ACFs, and CMEC SFs.
(E) GO Biological Process terms enriched in gene clusters from consensus matrix (padj < 0.05).
(F) KEGG pathways enriched in gene clusters from consensus matrix (padj < 0.05).
(G–I) Heatmaps showing expression of genes selected from GO: heart contraction (G); GO: regulation of ion transmembrane transport (H); and KEGG: adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes (I).