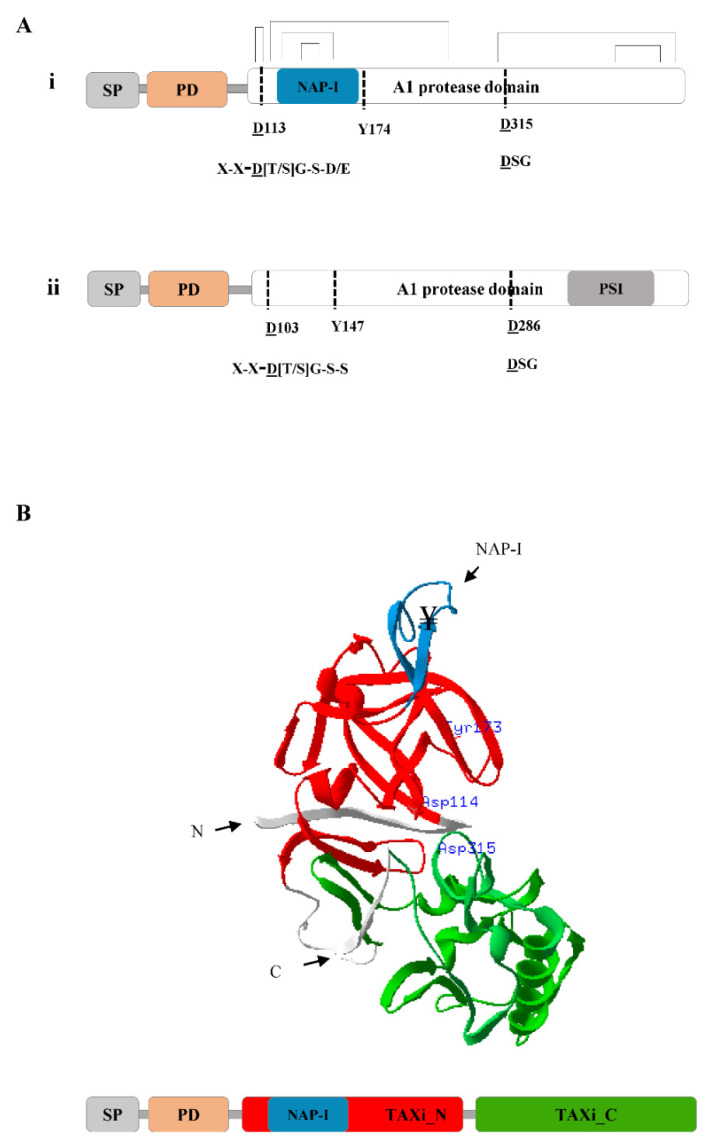
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the structure of nepenthesins (NEPs) and phytepsins (PEPs). (A) The primary structure organization of N. gracilis nepenthesin-2 (MER0031641) (i) and Cynara cardunculus phytepsin (MER0004937) (ii). Both proteins contain a signal peptide (SP), a prodomain (PD) and the A1 protease domain. The protease domain contains the two catalytic Asp residues (underlined) and the “flap” Tyr residue. The position of the PSI and NAP-I sequences are indicated for phytepsin and nepenthesin, respectively. The PEP and NEP signature motifs that contain the two catalytic Asp residues are indicated corresponding to the two Asp residues for both phytepsin and nepenthesin, (Ø- hydrophobic residue, D- Asp, T-Thr, G- Gly, Ser, E-Glu; [31]). (B) The tertiary structure of N. gracilis nepenthesin-2 protein predicted using Swiss PDB viewer [34]. The 3D annotation is based on the HMM based profile scan of the primary structure (shown below). In the primary structure, the position of the SP, PD, TAXi_N and TAXi_C, NAP-I sequence, and structurally important six disulfide bridges are shown. Two of the disulfide bridges are located in the NAP-I sequence. The TAXi_N and TAXi_C domains and the NAP-I sequence are colored in the 3D structure, consistent to the primary structure. The N- and C- termini and the active site residues (D113 Y174 D315) of the protein are also shown.