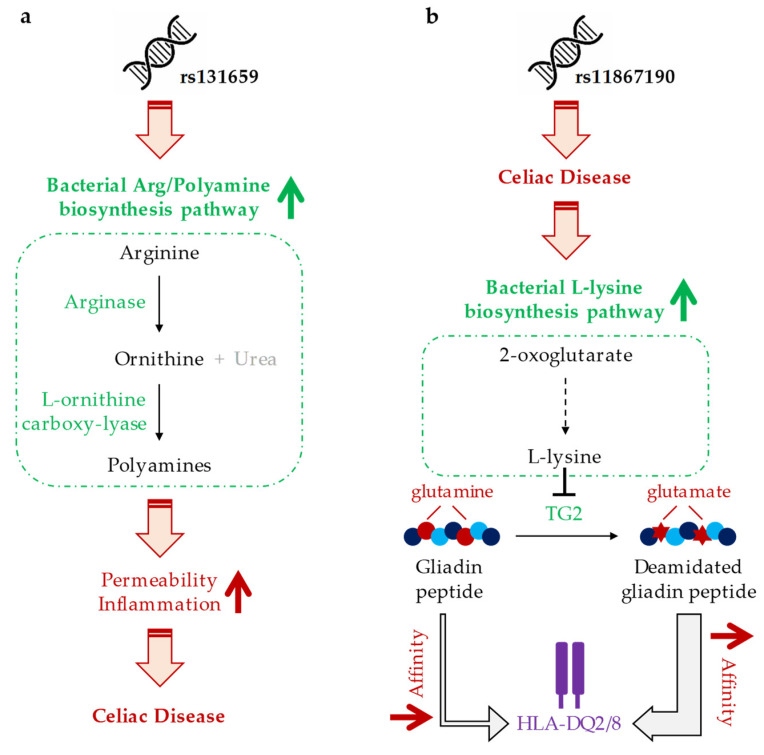
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the hypothetical mechanism of action of the identified SNP-microbiota associations. (a) rs131659 is associated with increased bacterial arginine/polyamine biosynthesis pathway, where arginine is converted to polyamines; by increasing permeability and inflammation, polyamines could play a role in CeD manifestation. (b) rs11867190 SNP is associated with CeD; increased production of L-lysine amino acid in the celiac intestine could be an adaptation of gut bacteria to counteract the activity of type 2 transglutaminase (TG2), which converts glutamines into glutamates; impaired TG2 activity would prevent the increase in the affinity of gliadin peptides for HLA-DQ2/8 receptors. HLA, human leukocyte antigen.