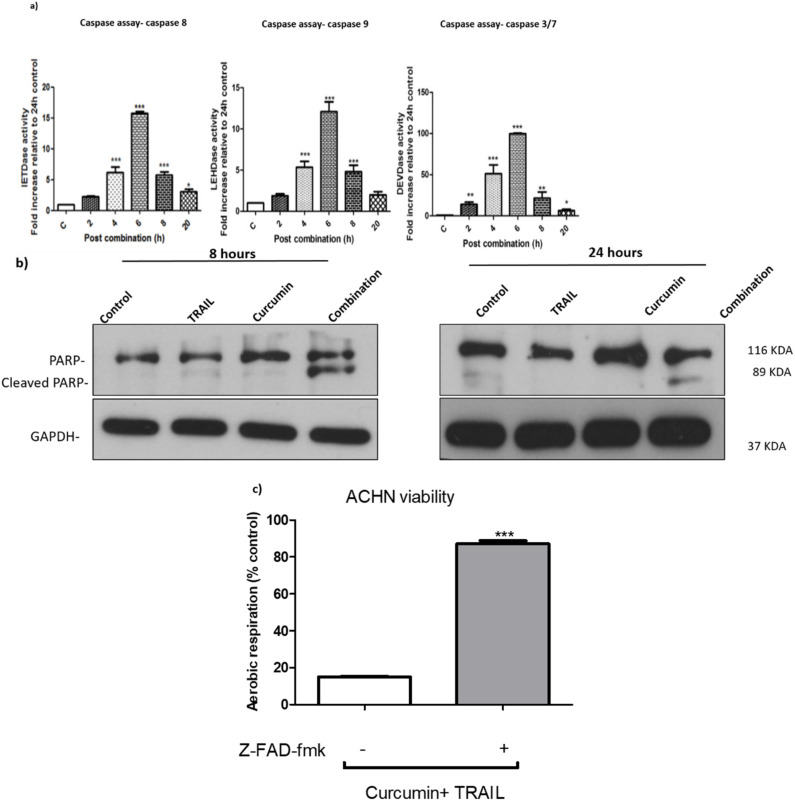
Figure 5.
Curcumin/TRAIL combination treatment induced apoptosis via induction of caspases activation (a) ACHN cells were cultured in six-well plates for 24 h. The cells were then incubated with culture medium containing 0.5% DMSO or 25 µM curcumin for 4 h, followed by a further incubation vehicle or 50 ng/mL TRAIL for a further 2, 4, 6, 8 and 20 h. Fluorescence was kinetically detected by a scanning fluorescent microplate reader for a period of 120 min (120 cycles, one measurement per minute) at 37 °C at an emission and excitation of 400 and 505 nm, respectively. The results were normalized against protein content and presented as mean ± SEM of five independent experiments. One-way ANOVA was used to analyse the data (b) ACHN cells were cultured on six-well plates and treated with culture medium containing 0.5% DMSO, 50 ng/mL TRAIL, 25 µM curcumin or a co-treatment of 50 ng/mL TRAIL/25 μM curcumin. Whole cell protein was extracted at 8 and 24 h with RIPA buffer. Equal amounts of protein were separated by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose and indirectly probed for PARP using monoclonal antibodies. GAPDH was employed as a loading control. A representative blot is shown from three independent experiments. (c) ACHN cells were cultured on six-well plates either pre-treated with vehicle or 200 µM z-VAD-fmk for 1 h, then incubated with 25 µM curcumin for 4 h, followed by a further incubation with 50 ng/mL TRAIL for up to 24 h. Cell viability was assessed using FluoroFire-Blue ProViaTox Resazurin Fluorescent assay. *, ** and *** indicate statistically significant differences from control at p < 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively. Independent t-test was employed to analyse the data.