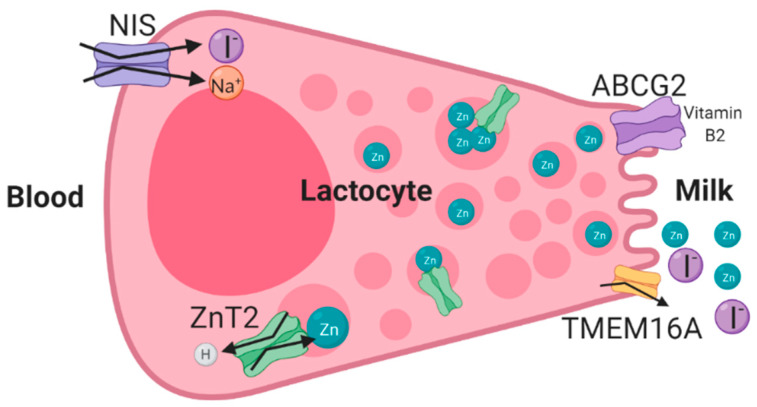
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the mechanism of transport of micronutrients in human lactocytes during lactation. ATP-driven, multidrug efflux transporter (ABCG2) [38,154], NIS [51,61], and ZnT2 transporter [21,155] were shown to transport riboflavin (vitamin B2), iodine, and zinc, respectively, in human mammary gland epithelial cells during lactation. The anion transporter TMEM16A is predicted to transport iodine into human milk [47,48].