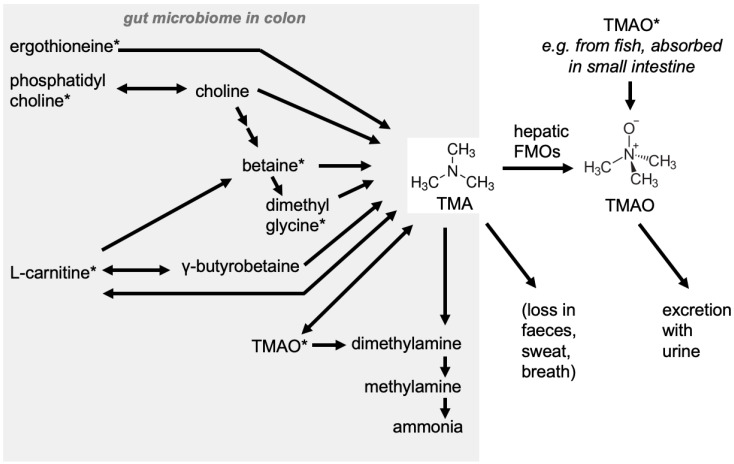
Figure 2.
Main biochemical conversions leading to trimethylamine (TMA) and TMAO. Modified from [37,38]. The compounds with an asterisk can originate from the diet. The conversions within the grey box (gut microbiome) are induced by the microbiota (mainly Firmicutes, Proteobacteria), and the resulting TMA is absorbed within the colon and converted to TMAO by liver FMOs (flavin monooxygenases). The possibly partial microbial degradation of TMA and TMAO (by methylotrophs and other occasional bacteria (Pseudomonas/Bacillus)) can result in the formation of formaldehyde within the colon; also, methylamines (including TMA/TMAO) could be substrates for the formation of nitrosamines [32,39]. If TMA is absorbed from the colon, 95% of it is converted to TMAO, which is then excreted in the urine [34]. Arrows pointing in two directions: reactions go in both directions.