Figure 1.
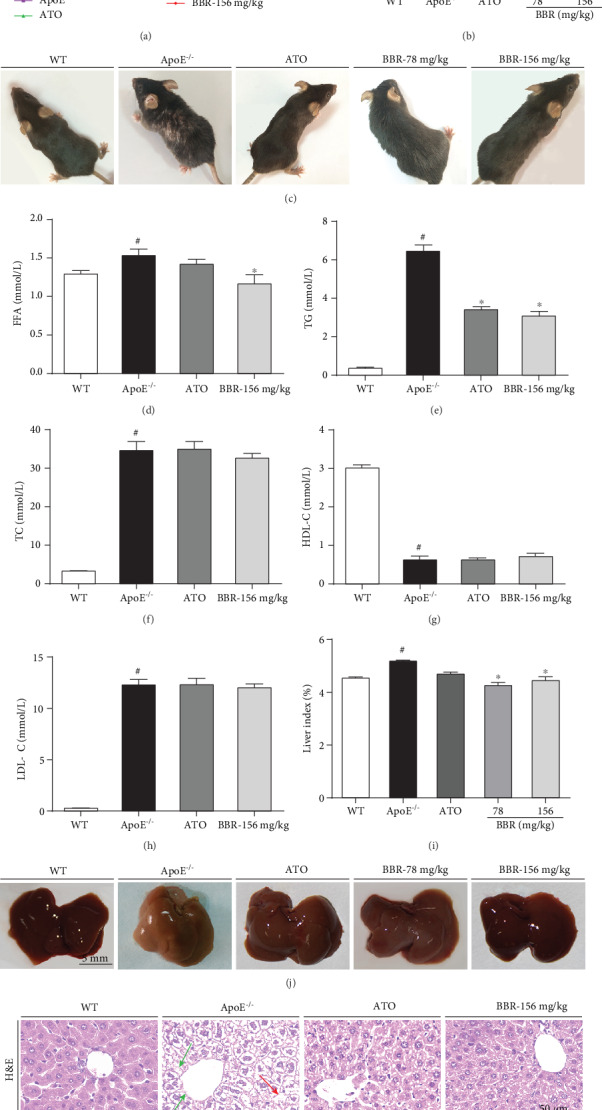
Berberine reduced serum lipid levels and antagonized hepatic lipid accumulation in ApoE−/− mice. Male wild-type C57BL/6 mice fed a normal chow diet and ApoE−/− mice fed a western-type diet in the presence and absence of berberine (78 and 156 mg·kg−1) or the presence of atorvastatin were administered by oral gavage for 12 weeks. (a) Body weight changes during the 12-week treatment (n = 15 in the WT, ApoE−/−, ATO, and BBR-156 mg·kg−1 groups; n = 7 in the BBR-78 mg·kg−1 group). (b) Body weight at 12 weeks of administration (n = 15 in the WT, ApoE−/−, ATO, and BBR-156 mg·kg−1 groups; n = 7 in the BBR-78 mg·kg−1 group). (c) Mice photos. (d–h) Serum levels of FFA, TG, TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C (n = 8). (i) Liver index (n = 12 in the WT, ApoE−/−, ATO, and BBR-156 mg·kg−1 groups; n = 6 in the BBR-78 mg·kg−1 group). (j) Liver photos. (k) Representative photomicrographs of H&E (top) and Oil Red O (bottom) staining of liver; magnification: 400x. The red arrow shows steatosis, and the green arrow shows inflammatory cell infiltrations in the liver. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. #P < 0.05 versus WT and ∗P < 0.05 versus ApoE−/−. WT: wild-type; BBR: berberine; ATO: atorvastatin; FFA: free fatty acids; TG: triglyceride; TC: total cholesterol; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
