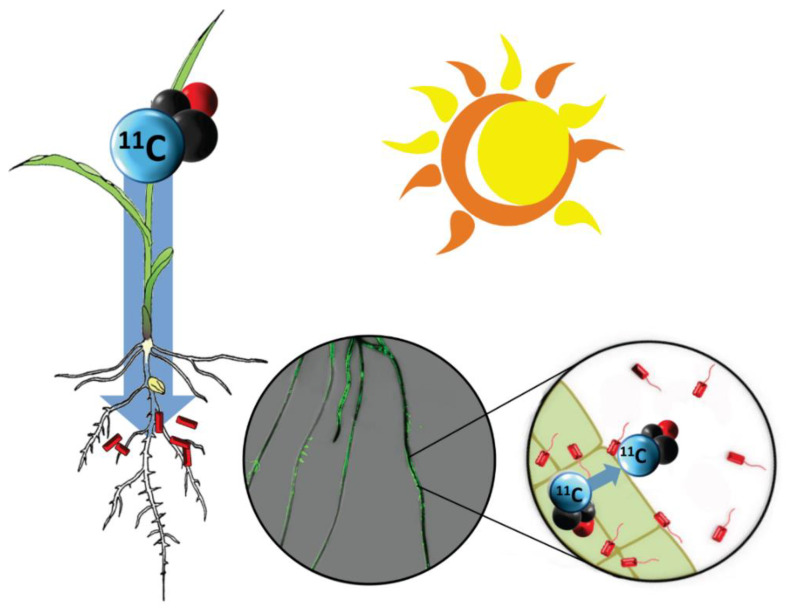
Figure 1.
Concept of plant-borne carbon tracing to root-associating rhizobacteria. Atmospheric carbon is traced from plant fixation of radioactive 11CO2 through root translocation as complex 11C-photosynthates. There, that carbon source is assimilated by root-associating microorganisms. The center insert shows an overlay of images from 11C-radiography (dark black regions reflect high levels of 11C activity) and a green fluorescence image arising from RAM10, a green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporting strain of H. seropedicae bacteria. Regions of high root colonization seem to draw more 11C.