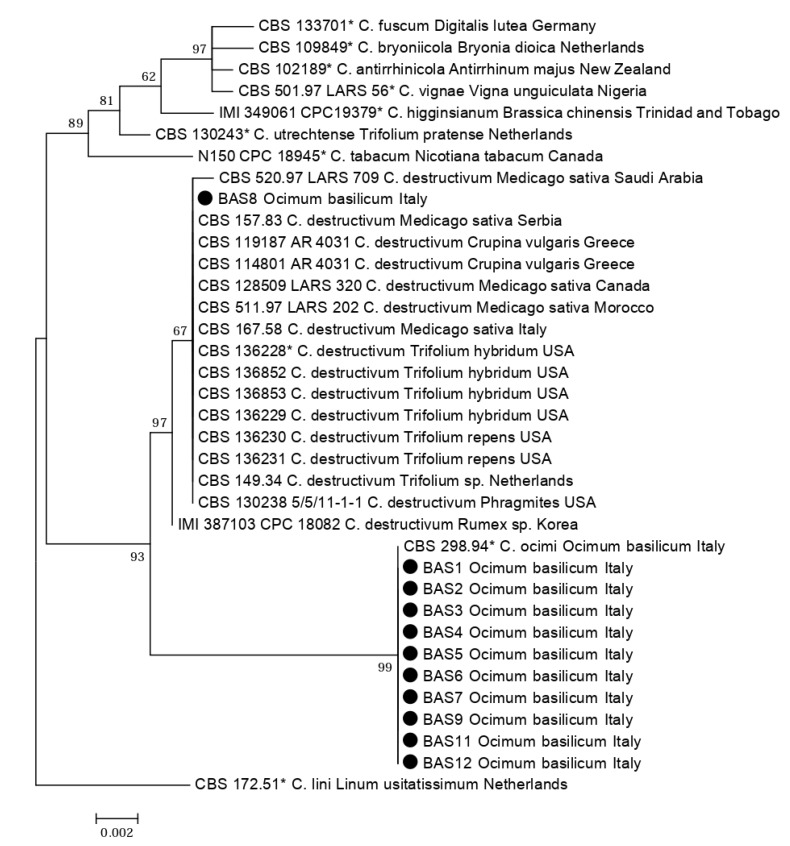
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree obtained using combined internal transcribed spacers (ITS) and β-tubulin (TUB2) sequences of isolates of Colletotrichum spp. collected in the present study from leaves of Ocimum basilicum (black dots) along with reference isolates of C. ocimi, C. destructivum, and other representative species of the C. destructivum species complex [24]. An isolate of C. lini is used as an outgroup. The evolutionary history was inferred using the maximum likelihood method based on the Tamura–Nei model and the tree with the highest log likelihood is shown. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. The asterisks (*) indicate the ex-holotype, ex-epitype or ex-neotype cultures.