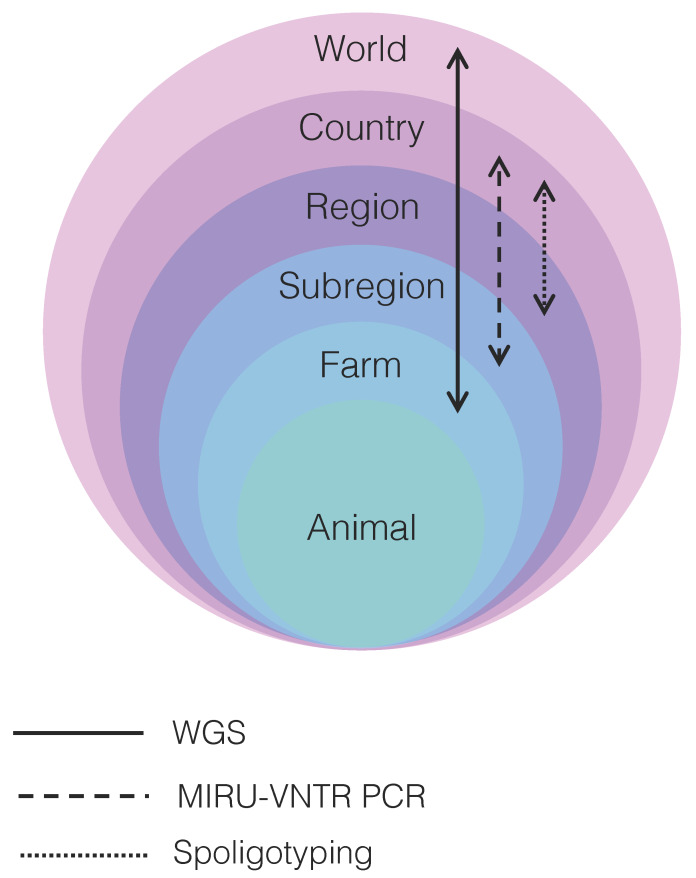
Figure 1.
Resolution power of the main techniques used to resolve transmission clusters of Mycobacterium bovis depicted in relation to world, country, region, subregion, farm, and animal levels. WGS: whole-genome sequencing; MIRU-VNTR: mycobacterial interspersed repetitive unit-variable-number tandem repeat typing; PCR: polymerase chain reaction. Arrows indicate the level of resolution each technique is able to achieve. WGS provides fine resolution to discriminate between M. bovis strains distributed globally to the individual farm level, while MIRU-VNTR PCR and spoligotyping have more limited resolution, particularly at the individual farm level. WGS may be able to discriminate between different M. bovis strains infecting the same animal only if sampling is comprehensive, multiple isolate cultures are sequenced, and/or deep sequencing of the primary isolate is performed.