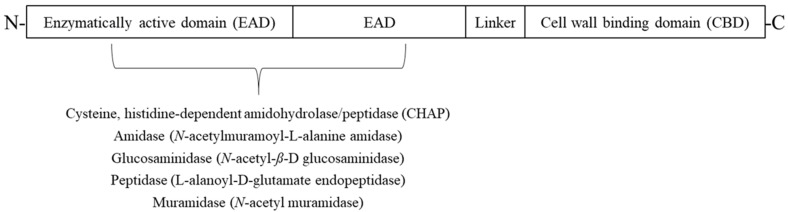
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the modular structure of phage-encoded peptidoglycan hydrolases. Most endolysins contain one or two enzymatically active domain (EAD) in N-terminal those cleave one of the bonds in the bacterial peptidoglycan, and one cell wall binding domain (CBD) involved in host bacterial recognition in C-terminal region. EAD and CBD are connected by a short linker.