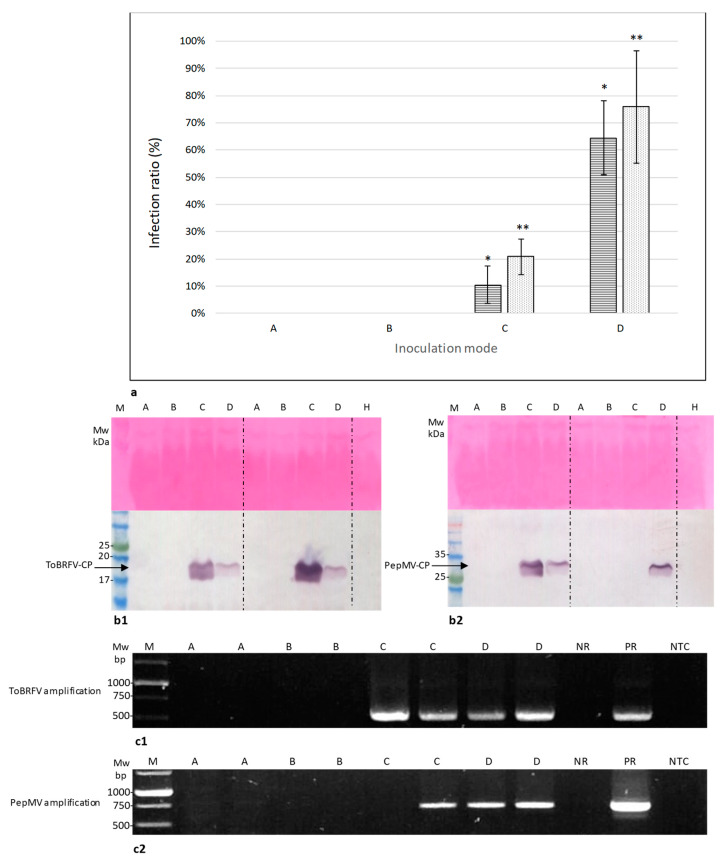
Figure 4.
Pepino mosaic virus (PepMV) and tomato brown rugose fruit virus (ToBRFV) infectivity potential of the symptomatic tomatoes. (a) A graph of ToBRFV and PepMV infection ratio means ± standard deviations, using A–D inoculation modes, as calculated from exp. 1–4 (presented in Table 2); (b) Western blot analyses of tomato plants inoculated by two different fruits using A–D inoculation modes. (c) RT-PCR analyses of tomato plants inoculated by two different fruits using A–D inoculation modes. (c1) RT-PCR amplified 615bp segments of ToBRFV CP. (c2) RT-PCR amplified 650 bp segments of PepMV CP. A, rubbing leaves with intact symptomatic fruits; B, rubbing leaves with hands after touching intact symptomatic fruits; C, applying symptomatic fruit juice onto tomato leaves; D, rubbing leaves with symptomatic fruit juice; M, molecular weight; H, healthy leaves; ToBRFV is marked with dots; PepMV is marked with horizontal lines; * p < 0.05 (p = 0.0266), t-test comparing PepMV inoculation modes C and D; ** p < 0.05 (p = 0.008), t-test comparing ToBRFV inoculation modes C and D. Bars are standard deviation of the mean. H, healthy tomato plants; NR, negative reference; PR, positive reference; NTC, non-template control.