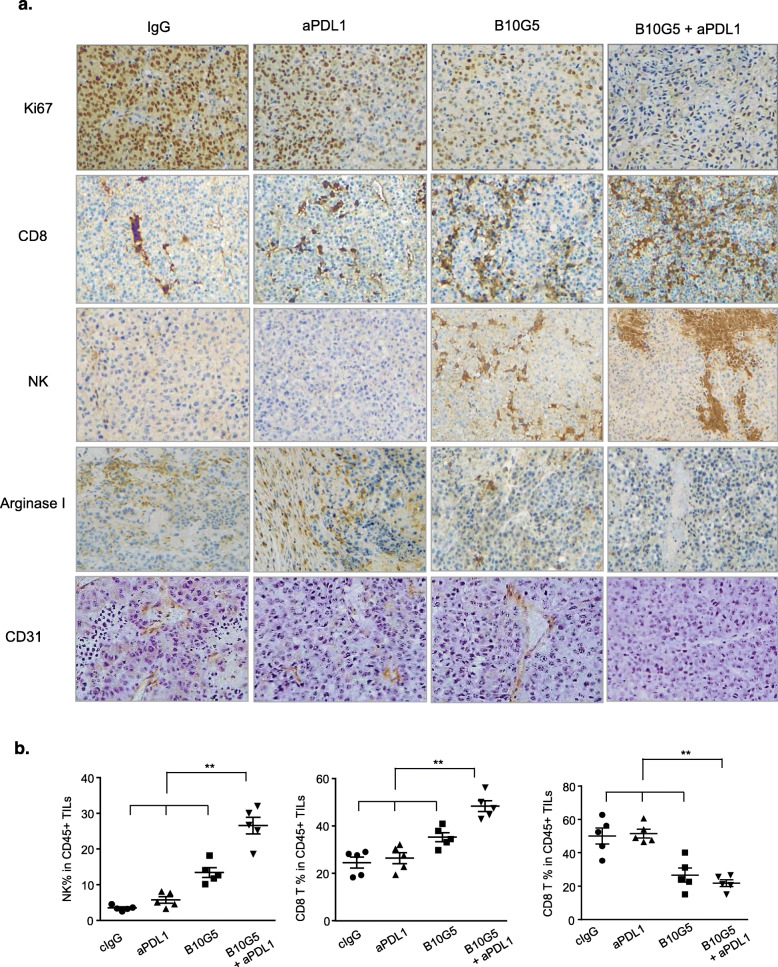
Fig. 2.
Combined therapy of B10G5 targeting sMIC and anti-PDL1 results in reduced tumor proliferation and a more immune primed tumor microenvironment with decreased neovascularization. a Representative micrographs of immunohistochemistry staining (IHC) of subcutaneous B16-sMICB tumors demonstrating that combined therapy resulted in reduced tumor cell proliferation as shown by Ki67 staining, increased NK and CD8 T cell, and decreased arginase 1+ cells in tumors. Combined therapy also decreased neovascularization within the tumor shown by CD31 staining. b Quantitation of NK cell, CD8 T cell, and the major arginase I producer MDSC in representative tumors by flow cytometry analyses. Data obtained at day 8 following treatment initiation in an experiment designed to understand therapeutic mechanisms as detailed in the text. *p < 0.05 as compared to the control group. **p < 0.05, combination therapy as compared to monotherapy