Fig. 4.
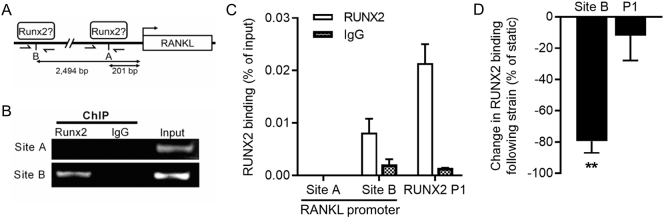
RUNX2 occupancy of the RANKL promoter decreases following strain. Schematic representation of the RANKL promoter that encompasses two RUNX2 recognition motifs (5′-ACCACA) denoted Site A (201 bp from the isoform 1 start site) and Site B (2,494 bp from the start site) in Saos-2 cells (A). Half-arrows indicate PCR amplicons amplified. Agarose gel images of PCR-amplified ChIPs with either RUNX2 antibody or IgG negative control antibody, and 1% input PCR positive control, using primer pairs specific for Site A or Site B in the RANKL promoter (B). PCR quantification of ChIPs with RUNX2 or IgG antibodies using RANKL promoter or the RUNX2 P1 promoter primers (ND = not detected) (C). Percent change in RUNX2 occupancy of the RANKL Site B and RUNX2 P1 promoter 8 h following strain (D). Bars represent the mean ± SEM, n = 3 representing three independent experiments. **p < .01 for the effect of strain.