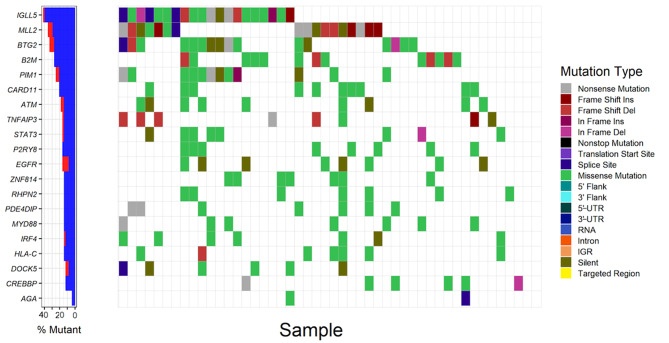
Figure 1.
Analysis of somatic mutations of the top 20 frequently mutated driver genes in patients with DLBCL (n=48). The left panel demonstrates the mutation rates of the 20 driver genes, blue and red denote synonymous and non-synonymous mutations respectively. The right panel demonstrates the distribution of mutations with different classes of functions in patient samples. UTR, untranslated region; IGR, intergenic region; DLBCL, diffuse large B cell lymphoma; Ins, insertion; Del, deletion; IGLL5, Immunoglobulin lambda like polypeptide 5; MLL2, myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia 2; BTG2, BTG anti-proliferation factor 2; B2M, beta-2-microglobulin; PIM1, Pim-1 proto-oncogene; CARD11, caspase recruitment domain family member 11; ATM, ATM serine/threonine kinase; TNFAIP3, TNF alpha induced protein 3; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; P2YR8, P2Y receptor family member 8; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ZNF184, zinc finger protein 184; RHPN2, rhophilin Rho GTPase binding protein 2; PDE4DIP, phosphodiesterase 4D interacting protein; MYD88, MYD88 innate immune signal transduction adaptor; IRF4, interferon regulatory factor 4; HLA-C, major histocompatibility complex class I C; DOCK5, dedicator of cytokinesis 5; CREBBP, CREB binding protein; AGA, aspartylglucosaminidase.