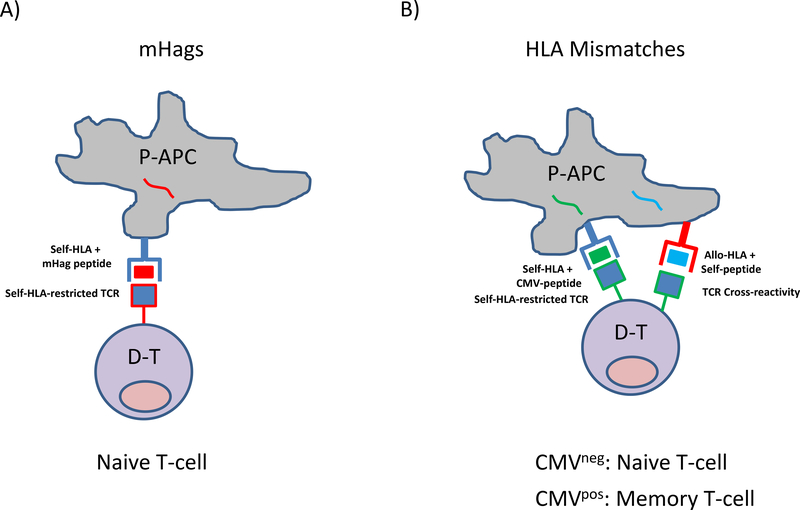
Figure 1. T-cell alloreactivity to mHAg or HLA-antigens mediating GvL and GvHD after HCT.
A) Self-HLA-restricted T-cell allorecognition of mHag peptides. Patient antigen-presenting-cells (P-APC) contain mHAg peptides (red) which are presented in the peptide-antigen binding groove of self-HLA-molecules (blue). HLA-matched donor T-cells (D-T) expressing a self-HLA-restricted T cell receptor (TCR) specific for the mHag peptide (red-lined blue square) recognize the mHAg-self-HLA complex on P-APC and mediate alloreactivity. Unless primed by previous events such as pregnancies or blood transfusions, the donor T-cells have not encountered the mHAg peptides before and are therefore in the naïve repertoire. B) Cross-reactive T-cell allorecognition of mismatched HLA-Antigens. Shown is a P-APC presenting, as an example, cytomegalovirus (CMV)-peptides (green) or self-peptides (blue) in the peptide-antigen-binding groove of self-HLA (blue) or allo-HLA molecules (red), respectively. D-T expressing a self-HLA-restricted TCR specific for the CMV-peptide (green-lined blue square) recognize the CMV-self-HLA complex on the P-APC, thereby mediating protective anti-viral immunity. In this example, the same TCR is also able to cross-recognize the allo-HLA presenting self-peptide due to molecular mimicry, thereby mediating alloreactivity. According to the donor’s CMV serostatus, the CMV-specific alloreactive T-cells will be predominant in the naive or in the memory compartment. CMV is shown here only as an example, self-HLA restricted T-cells specific for any foreign antigen can in principle display cross-reactive alloreactivity to mismatched HLA presenting self-peptides.