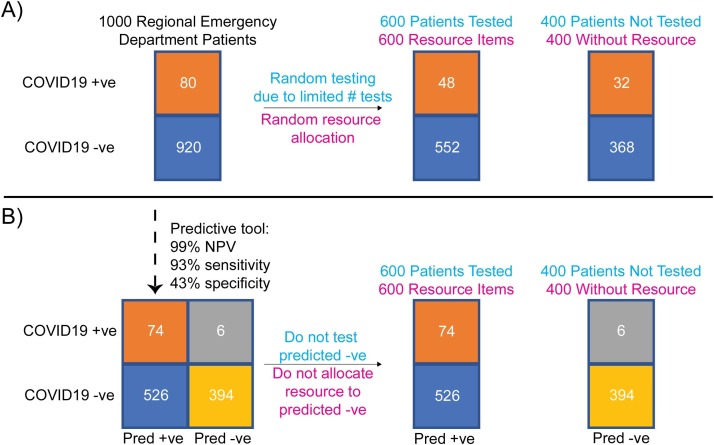
Fig. 1.
Value of a predictive COVID-19 rule-out tool in improving utilization of health care resources during a pandemic. Example contains a cohort comprising 1000 hypothetical patients with respiratory symptoms presenting to emergency departments across a region and assumes 8% COVID-19 prevalence, a highly accurate SARS-CoV-2 test, and 600 of a limited hospital resource (e.g. SARS-CoV-2 tests, personal protective equipment). (Panel A) If patients are randomly tested or randomly allocated a hospital resource during the wait for results, many patients with COVID-19 patients may not get tested or allocated the resource. (Panel B) With availability of a predictive tool of high sensitivity and negative predictive value based on readily available routine test results, utilization of limited confirmatory SARS-CoV-2 testing or other resources is reserved for those patients more likely to have COVID-19, with a 33 % improvement (48/80 to 74/80) in resource allocation. COVID19 +ve: COVID-19 positive patients; COVID19 -ve: COVID-19 negative patients; Pred + ve: predicted positive; Pred -ve: predicted negative.