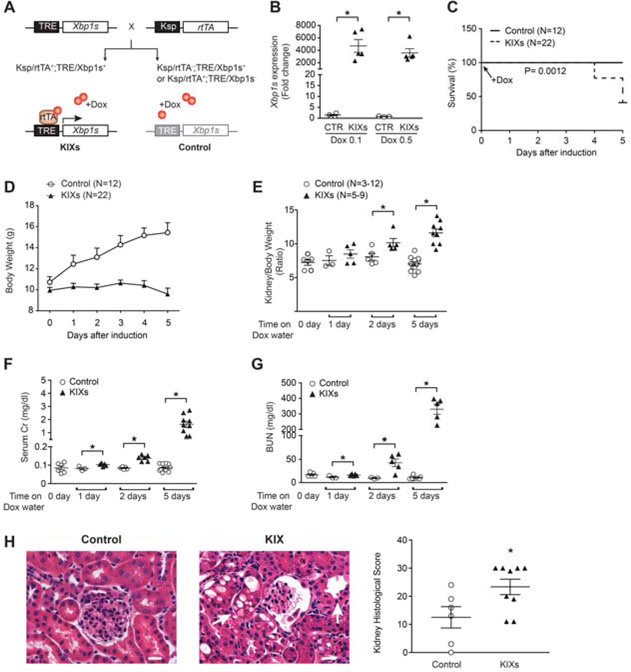
Figure 2. Overexpression of Xbp1s in the kidney produces tubular injury.
(A) To generate a kidney-inducible Xbp1s (KIX) mouse model, TRE/Xbp1s mice were crossed with Ksp/rtTA mice. KIXs were Ksp/rtTA;TRE-Xbp1s positive, whereas control animals only expressed either TRE-Xbp1s or Ksp/rtTA (lighter grey color). Doxycycline (Dox) was used to induce Xbp1s expression in renal tubular cells at postnatal day 21 (P21). Control animals also received Dox. (B) qPCR showed that Xbp1s expression increased equally after one day treatment with Dox- containing water at concentrations of either 0.1 mg/ml or 0.5 mg/ml. (C-G) 0.5 mg/ml Dox- containing water was provided daily for the duration of the experiment. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of KIXs and control mice upon treatment with Dox. The experiment was stopped after 5 days. (D) Body weight of KIXs and control mice upon Xbp1s induction. (E) Kidney to body weight ratios for KIXs and control mice at baseline and after Xbp1s induction. (F-G) Kidney function of KIXs and control mice was assessed by serum Cr (F) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN, G) levels. (H) H&E staining revealed histological changes consistent with acute tubular necrosis (e.g. tubule dilation and intracellular vacuoles; arrows) in KIXs mice at 5 days after induction. Kidney histological score is shown (control, n=6; KIXs, n=9). Scale bar, 20 μm. Bars and error bars are mean and SEM. Student’s unpaired t-test of KIXs vs. control at each time-point. * indicates P<0.05, compared to respective control. TRE: tetracycline responsive element; Ksp: Ksp-cadherin promoter; rtTA: reverse tetracycline-controlled transactivator; KIXs: kidney- inducible Xbp1s mice; Cr: creatinine.