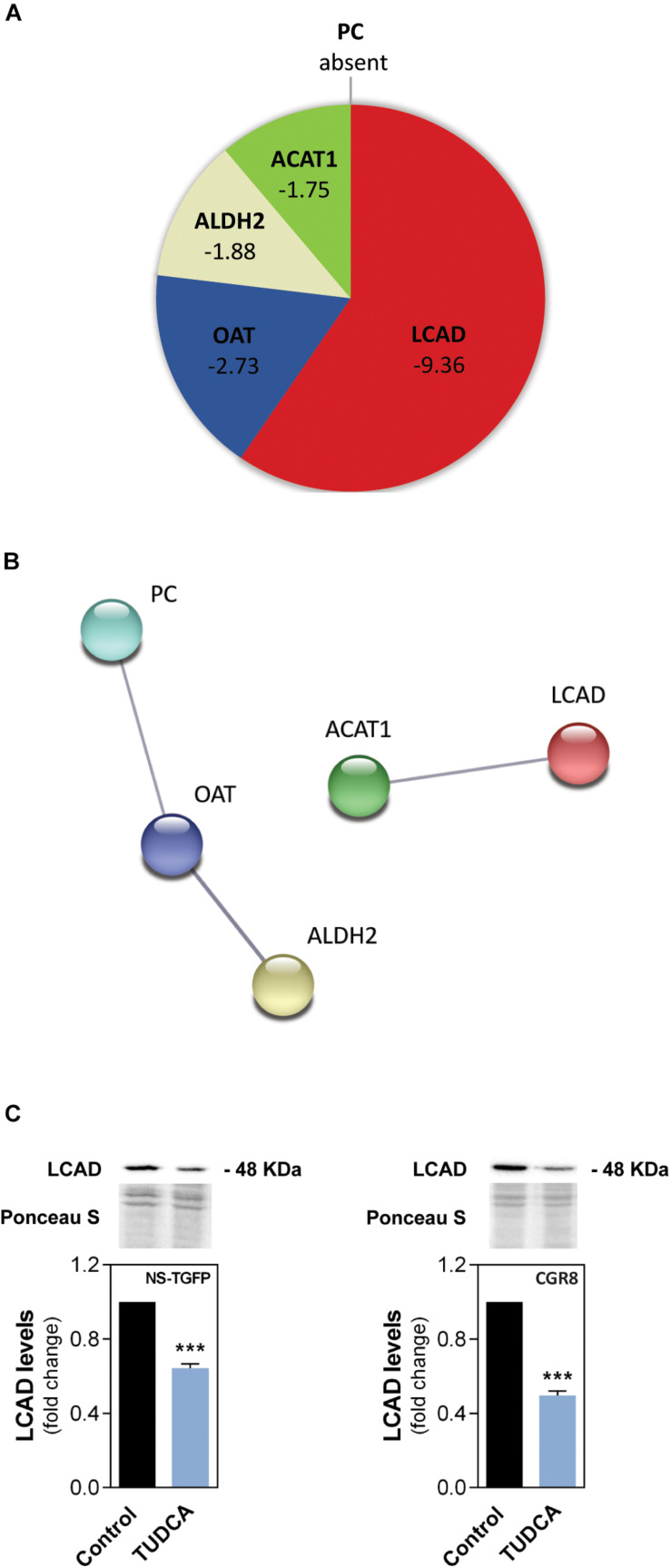
FIGURE 1.
The proliferation-inducing agent TUDCA downregulates a FA oxidation-associated enzyme in NSCs. Early-differentiating mouse NSC lines NS-TGFP and CGR8 were incubated with TUDCA for 24 h. Mitochondrial protein purified extracts were isolated for liquid chromatography mass spectrometry-based proteomics (LC-MS) and/or Western blot analysis, as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Pie diagram of the proteomic data showing the mitochondrial proteins significantly regulated by TUDCA in NS-TGFP cell line, and respective variations, when compared with control. The proteins were identified as the long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCAD), the ornithine aminotransferase (OAT), the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2), the acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase (ACAT1) and the pyruvate carboxylase (PC). Results are expressed as mean in fold-change, for at least three independent experiments, when compared with control (untreated cells). Significance threshold was set to p < 0.05 from control (untreated cells). (B) STRING analysis showing protein-protein network between the most regulated mitochondrial proteins by TUDCA in NSCs. Nodes represent proteins and lines connecting nodes indicate direct, or indirect interactions between proteins. Colorful nodes represent proteins that are downregulated or absent in TUDCA-treated NSCs. Functional protein network database version 10.0 (http://string-db.org, accessed in August 2019). (C) Representative immunoblots (top) of LCAD mitochondrial levels and respective densitometry analysis (bottom) in mitochondrial protein extracts from the NSC lines. LCAD levels were normalized to Ponceau S. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM fold-change for at least three independent experiments. ***p < 0.001 from control (untreated cells).