FIGURE 4.
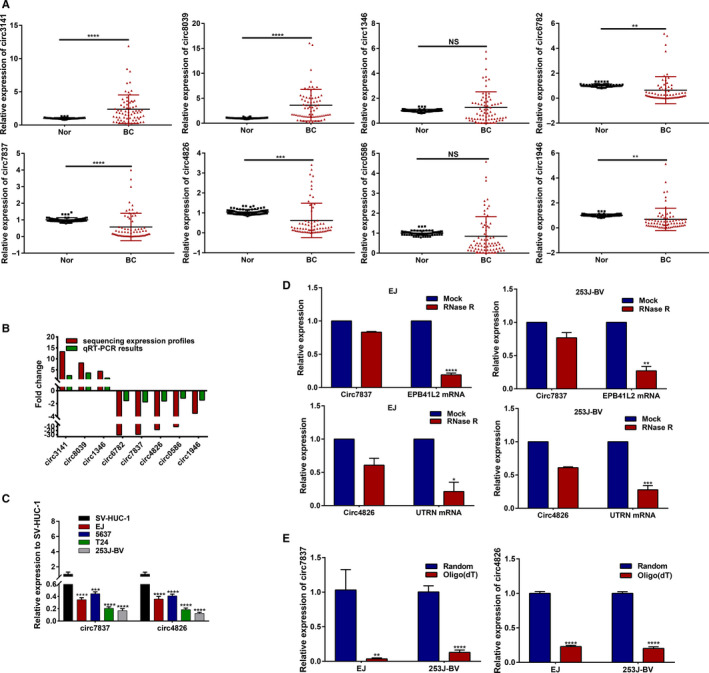
The relative levels of the selected eight circRNAs by real‐time qPCR (in triplicate) analysis. (A) Relative expression levels of them were determined in 70 pairs of BC specimens and nontumorous specimens. Circ‐3141, hsa_circ_0003141; Circ‐8039, hsa_circ_0008039; Circ‐6782, hsa_circ_0026782; Circ‐7837, hsa_circ_0077837; Circ‐4826, hsa_circ_0004826; Circ‐1946, hsa_circ_0001946. (B) Comparison of fold change (2−△△Ct) of circRNAs between qRT‐PCR results (n = 70 paired tissues) and our sequencing expression profiles (n = 5 paired tissues). (C) qRT‐PCR measurement of the expression levels of circ_0077837 and circ_0004826 among normal urothelial cell line (SV‐HUC‐1) and four malignant BC cell lines (EJ, HTB‐9, T24T, and 253J‐BV). (D) qRT‐PCR for the expression of circ_0077837, circ_0004826 and relevant EPB41L2, UTRN mRNA in EJ and 253J‐BV cells treated with or without RNase R. The results indicated that circ_0077837 and circ_0004826 was resistant to RNase R digestion. (E) Oligo (dT)18 primers or random hexamer were carried out in the reverse transcription experiments, respectively. For circ_0077837 and circ_0004826, the relative expression levels were analyzed by qRT‐PCR and normalized to the value through random hexamer primers
