Fig 3. Reduced viability in the absence of MUS81 is independent of Type I or Type II telomerase-deficient survivor formation.
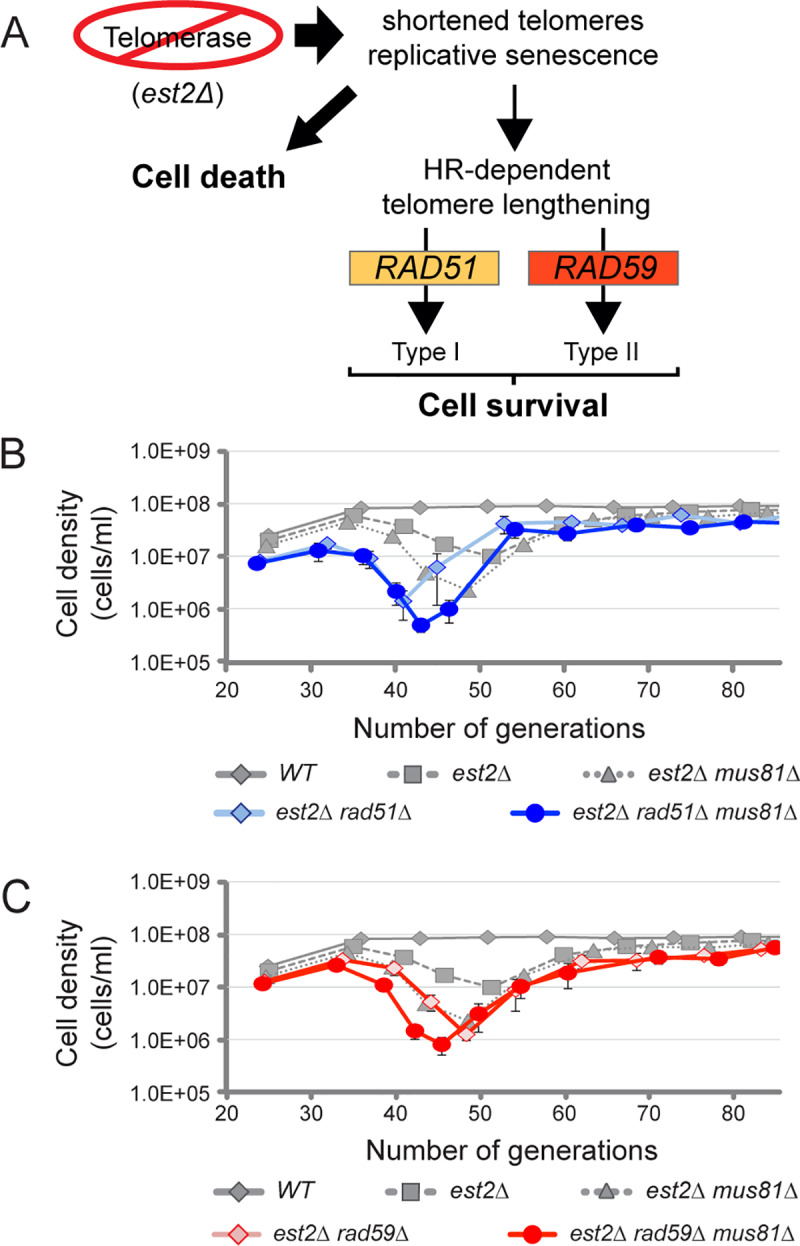
(A) Diagram of survivor formation in the absence of yeast telomerase. Genetic requirements are highlighted for RAD51 and RAD59 in Type I and Type II survivor formation, respectively. Arrow size represents abundance of cells entering cell death or survival via homologous recombination (HR)-mediated telomere lengthening. (B) Average cell densities are plotted with one standard of error for wild type (WT) (n = 20), est2Δ (n = 40), est2Δ mus81Δ (n = 27), and est2Δ rad51Δ (n = 8), and est2Δ rad51Δ mus81Δ (n = 10), or (C) est2Δ rad59Δ (n = 9) and est2Δ rad59Δ mus81Δ (n = 9). Yeast strains rad51Δ, mus81Δ rad51Δ, est2Δ rad51Δ, and est2Δ rad51Δ mus81Δ strains were derived from diploid WDHY3358 as described in Materials and Methods. Remaining haploid strains, est2Δ rad59Δ, and est2Δ rad59Δ mus81Δ, were derived from WDHY3366, and est2Δ mus81-dd was derived from WDHY3007. WT and est2Δ strains were derived from sporulation of all three diploids.
