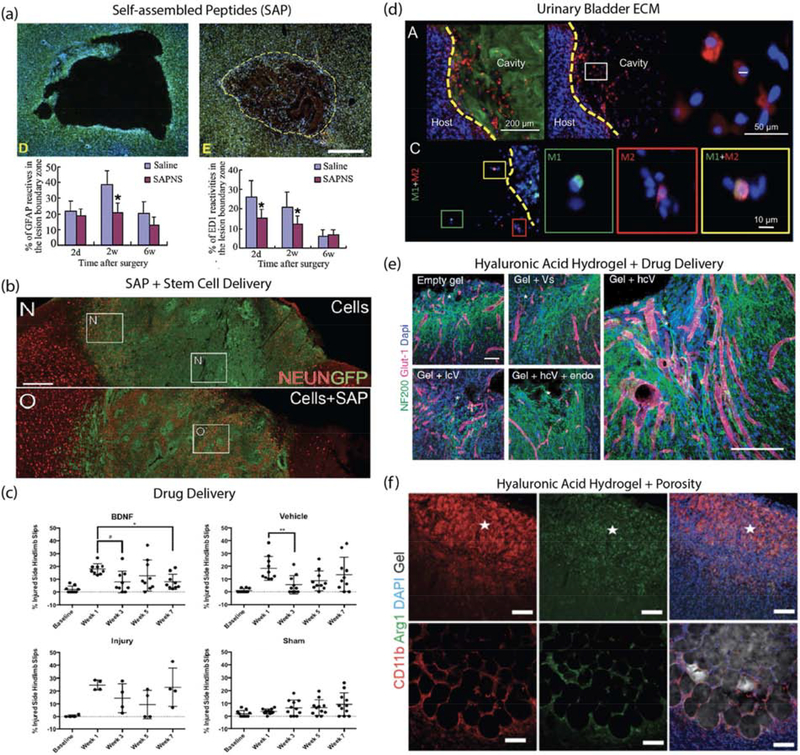
Figure 2.
Material examples for brain repair after stroke. (a) RADA16 self-assembled peptide nanofiber scaffold (SAPNS): Nissl and DAPI stained images of saline-injected lesion and SAPNS-injected lesion as well as quantification of astrocytes (GFAP positive) and macrophages (ED1 positive) in the lesion boundary zone at 2 days, 2 weeks and 6 weeks after treatment. Source: Adapted from [44]. (b) IKVAV self-assembled peptide (SAP) and human cortical progenitor: NeuN stained images comparing GFP-labelled human cortical progenitors in stem cell delivery vs stem cell+SAP. Image shows increased proportion of NeuN-positive cells in SAP group. Source: Adapted from [36]. (c) BDNF-loaded hyaluronan-methylcellulose and PLGA nanoparticle scaffold composite: Behavioral studies after local BDNF delivery via material vehicle showed improvement in hindlimb recovery following stroke injury. Source: Adapted from [23]. (d) Urinary bladder matrix-ECM hydrogel: Immunostained images showing ECM hydrogel (Collagen I), cell nucleus (DAPI), macrophage/microglia (Iba-1), M1-like phenotype (CD86) and M2-like phenotype (CD206). Quantification of results showed that ECM hydrogel modulated neuroinflammation. Source: Adapted from [35]. (e) Hyaluronic acid and clustered VEGF on heparin nanoparticle hydrogel: Immunostained images of neurons (NF200 positive) and vessels (Glut-1 positive) in stroke infarct showed gel + high cluster VEGF delivery resulted in enhanced angiogenesis, neurogenesis and axonal sprouting. Source: Adapted from [41]. (f) Microporous annealed particles (MAP) hydrogel: Immunostained images of sham and MAP-treated stroke lesions showing gel, cell nucleus (DAPI), macrophage/microglia (CD11b) and pro-repair phenotype (Arg1). Quantification showed material modulated neuroinflammation by increasing pro-repair macrophage/microglia in the stroke infarct. Source: Adapted from [38].