Figure 2.
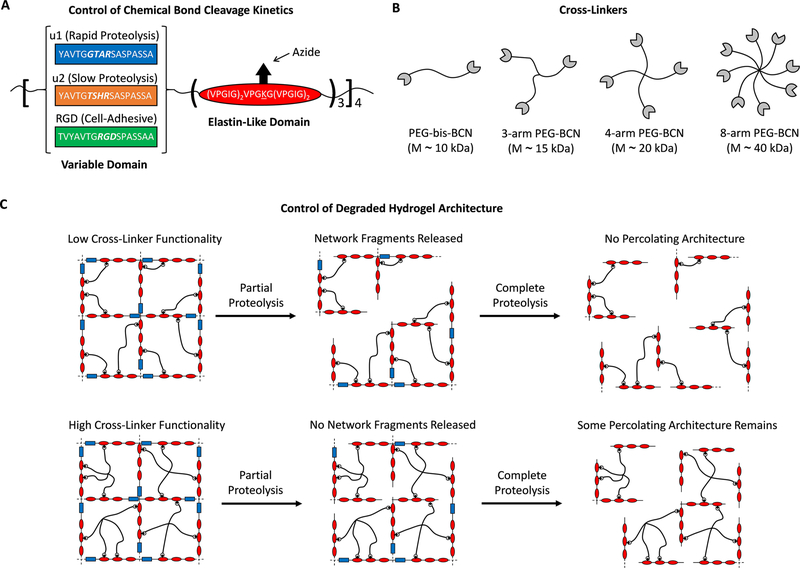
(A) Engineered elastin-like proteins (ELPs) enable simultaneous tuning of peptide bond cleavage rate, cell adhesivity, and hydrogel network architecture through modular design. Primary amines on the ELPs are functionalized with azides to permit cross-linking via SPAAC. (B) Multiarm PEGs functionalized with bicyclononynes serve as cross-linkers to control network connectivity while keeping molecular weight between cross-links (and hence mesh size) constant. (C) The maximal degradable fraction of the network is controlled by altering cross-linker functionality. Increasing the cross-linker functionality increases the redundant connections within the network, decreasing the fraction of the network able to be released and retaining the percolating achitecture.