Figure 5. Metabolism and epigenetic regulation.
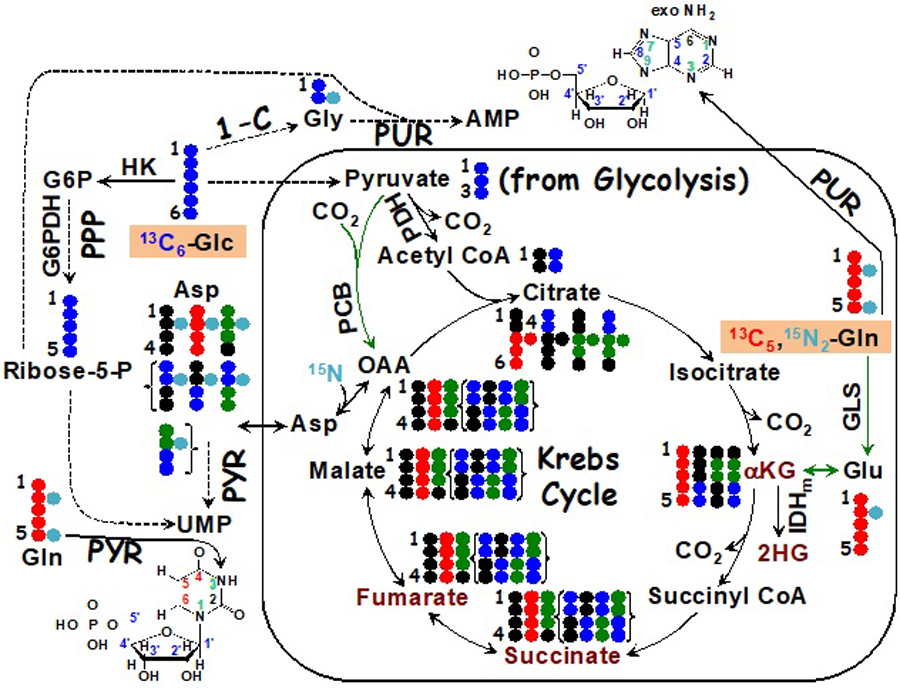
The diagram depicts 13C tracing from 13C6-glucose ( ) or 13C/15N tracing from 13C5,15N2 glutamine (
) or 13C/15N tracing from 13C5,15N2 glutamine ( ) to the synthesis of nucleotides and effectors (dark red text) involved in epigenetic modifications, including αketoglutarate (αKG), 2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG), succinate, and fumarate. IDH1/2 mutants produce the histone demethylation inhibitor 2HG from αKG while inactivating SDH and FH mutations generate high levels of succinate and fumarate, which are inhibitors of αKG-dependent dioxygenases including TET involved in demethylation of methylcytosine in DNA. Green arrows denote anaplerotic inputs into the Krebs cycle mediated by pyruvate carboxylase (PCB) (
) to the synthesis of nucleotides and effectors (dark red text) involved in epigenetic modifications, including αketoglutarate (αKG), 2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG), succinate, and fumarate. IDH1/2 mutants produce the histone demethylation inhibitor 2HG from αKG while inactivating SDH and FH mutations generate high levels of succinate and fumarate, which are inhibitors of αKG-dependent dioxygenases including TET involved in demethylation of methylcytosine in DNA. Green arrows denote anaplerotic inputs into the Krebs cycle mediated by pyruvate carboxylase (PCB) ( ) and glutaminase (GLS) reactions. { } encloses scrambled 13C labeling patterns of succinate, fumarate, malate, and Asp after one turn of the Krebs cycle. ●: 12C; OAA: oxaloacetate; HK: hexokinase; G6PDH: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; IDHm: isocitrate dehydrogenase mutant; PUR: purine synthesis; PYR: pyrimidine synthesis; PPP: pentose phosphate pathway; 1-C: one-carbon pathway; exo: exocyclic.
) and glutaminase (GLS) reactions. { } encloses scrambled 13C labeling patterns of succinate, fumarate, malate, and Asp after one turn of the Krebs cycle. ●: 12C; OAA: oxaloacetate; HK: hexokinase; G6PDH: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; IDHm: isocitrate dehydrogenase mutant; PUR: purine synthesis; PYR: pyrimidine synthesis; PPP: pentose phosphate pathway; 1-C: one-carbon pathway; exo: exocyclic.
