Figure 6. SIRM study on patient-derived organoids (PDO) in response to anti-cancer selenite.
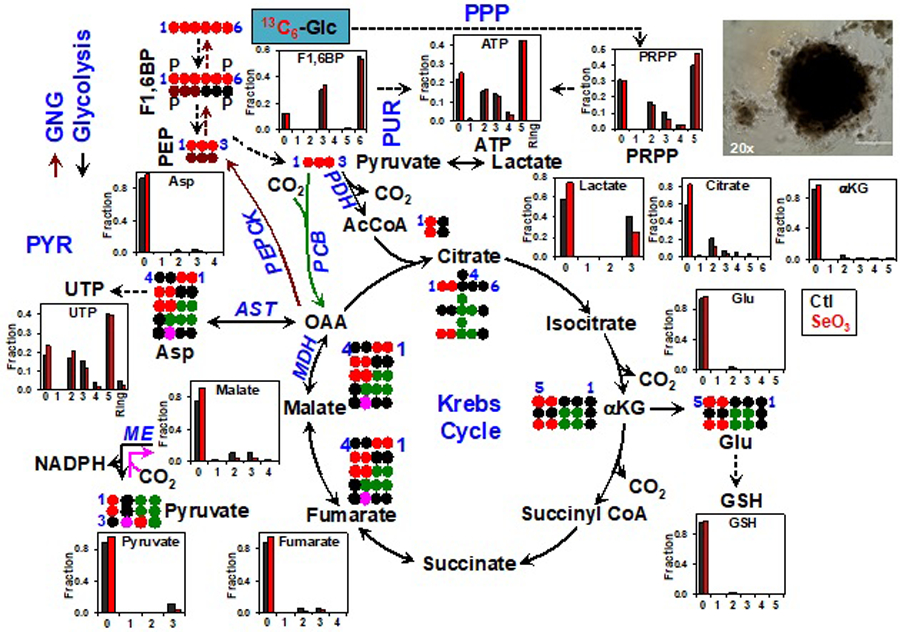
PDO was isolated from a non-small cell lung cancer patient (UK022) tumor xenograft in Matrigel and subsequently grown as M3DB cultures (example 20x image shown) in [13C6]-Glc+DMEM medium ± 10 µM selenite (SeO3) for 48 hr. Atom-resolved tracing from [13C6]-Glc to glycolytic, Krebs cycle, and gluconeogenic (GNG) metabolites is shown along with the 13C labeling patterns of these metabolites in response to SeO3. Also shown are the SeO3-induced changes in 13C labeling patterns of the products of PPP, purine (PUR)/pyrimidine (PYR) synthesis, and glutathione (GSH) synthesis. The numbers in X-axis represent the number of 13C atoms (isotopologues) in each metabolite while “Ring” in ATP and UTP indicates the sum of all 13C-nucleobase isotopologues.  denote GNG and anaplerotic inputs into the Krebs cycle mediated by PCB, respectively. ●: 12C;
denote GNG and anaplerotic inputs into the Krebs cycle mediated by PCB, respectively. ●: 12C;  : PDH-, PCB-, or malic enzyme (ME) initiated Krebs cycle reactions, respectively;
: PDH-, PCB-, or malic enzyme (ME) initiated Krebs cycle reactions, respectively;  : GNG; F1,6BP: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate; PRPP: phosphoribosylpyrophosphate; PEPCK: PEP carboxykinase; MDH: malate dehydrogenase; AST: aspartate amino transferase. All other symbols and abbreviations are as in Fig. 5.
: GNG; F1,6BP: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate; PRPP: phosphoribosylpyrophosphate; PEPCK: PEP carboxykinase; MDH: malate dehydrogenase; AST: aspartate amino transferase. All other symbols and abbreviations are as in Fig. 5.
