Table 1.
Summary of medicinal thiols and their current and potential uses.
| Common Name | Structure | Primary Use | Primary Mechanism | Other Uses Covered in this Review |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-Acetyl-L-cysteine | 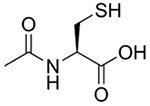 |
APAP overdose [16, 18, 21, 23, 25, 29, 32, 34, 36, 38–42, 45–51, 53] | Acts as GSH prodrug by supplying cysteine | Lead toxicity [82, 85–86] Radioprotection [129, 146–147] Psychiatric/Neurologic Disorders [170, 171] |
| Amifostine, WR-2721 | Radioprotection [113, 119, 121–134] | Scavenges free radicals formed during RT | - | |
| Captopril | 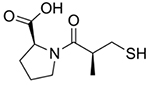 |
Hypertension [163, 165–166] | Blocks activation of angiotensin, a vasoconstrictor | Lead toxicity [89] Radioprotection [136–139] Metallo-β-lactamase inhibition [167–169] Alzheimer’s/dementia [173, 174] |
| Dimercaprol, BAL in oil | 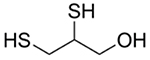 |
Heavy metal toxicity As, Au, Hg, and Pb [71–72, 94–96] | Chelates heavy metals, facilitating their removal | - |
| 2,3-meso- Dimercaptosuccinic acid |
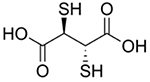 |
Lead poisoning [71–72, 74, 76–81] | Chelates Pb to form soluble, excretable complexes | - |
| N-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)-glycine, Tiopronin, Thiola | 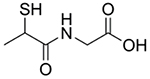 |
Cystinuria [157–158] | Forms soluble cysteine-tiopronin disulfides with excess cysteine in urine | Metallo-β-lactamase inhibition [167] Copper chelation [159] |
| D-Penicillamine | 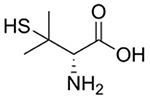 |
Wilson’s disease [97, 99, 101–102, 104, 106, 108, 110] | Chelates Cu to form soluble, excretable complexes | Rheumatoid arthritis [151–155] Chemotherapy adjuvant [98] |
