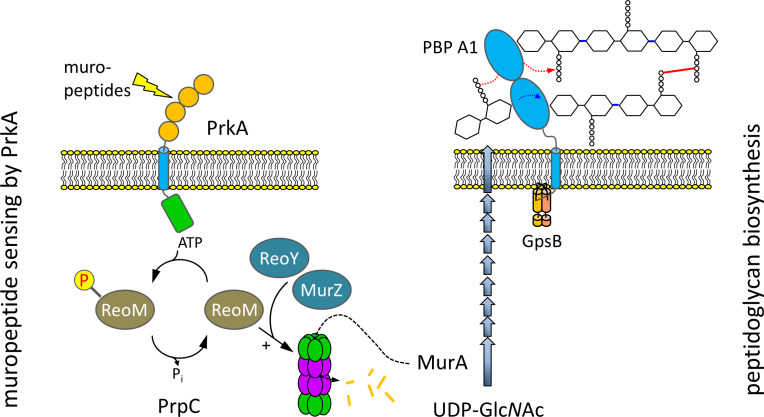
Figure 9. ReoM links PrkA-dependent muropeptide sensing with peptidoglycan biosynthesis.
Model illustrating the role of ReoM as substrate of PrkA and as regulator of ClpCP. PrkA recognises free muropeptides, which activate PrkA to phosphorylate ReoM. In its unphosphorlyated form, ReoM is an activator of ClpCP-dependent degradation of MurA, the first enzyme of peptidoglycan biosynthesis, and ReoY and MurZ contribute to this process. By phosphorylating ReoM, PrkA prevents ClpCP-dependent MurA degradation so that MurA accumulates and peptidoglycan biosynthesis can occur. Please note that there is a lesser degree of conservation in the fourth PASTA domain of PrkA.