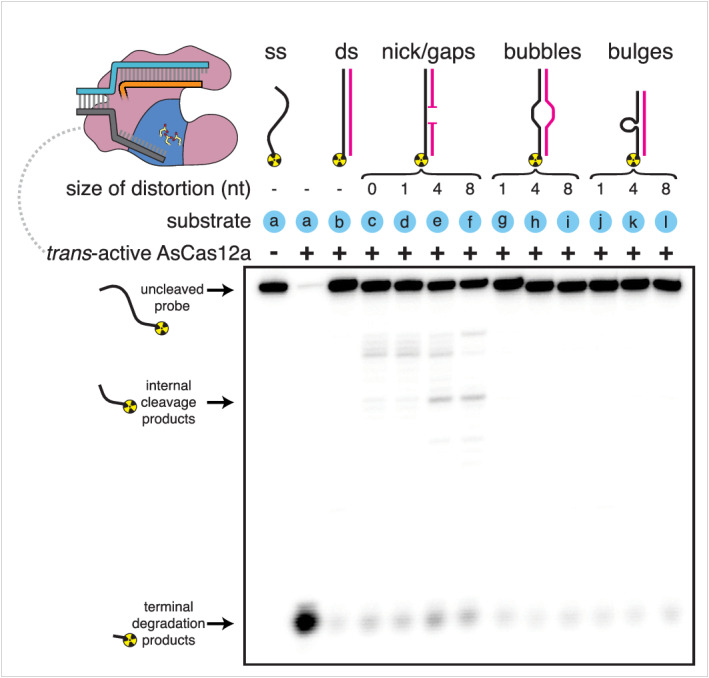
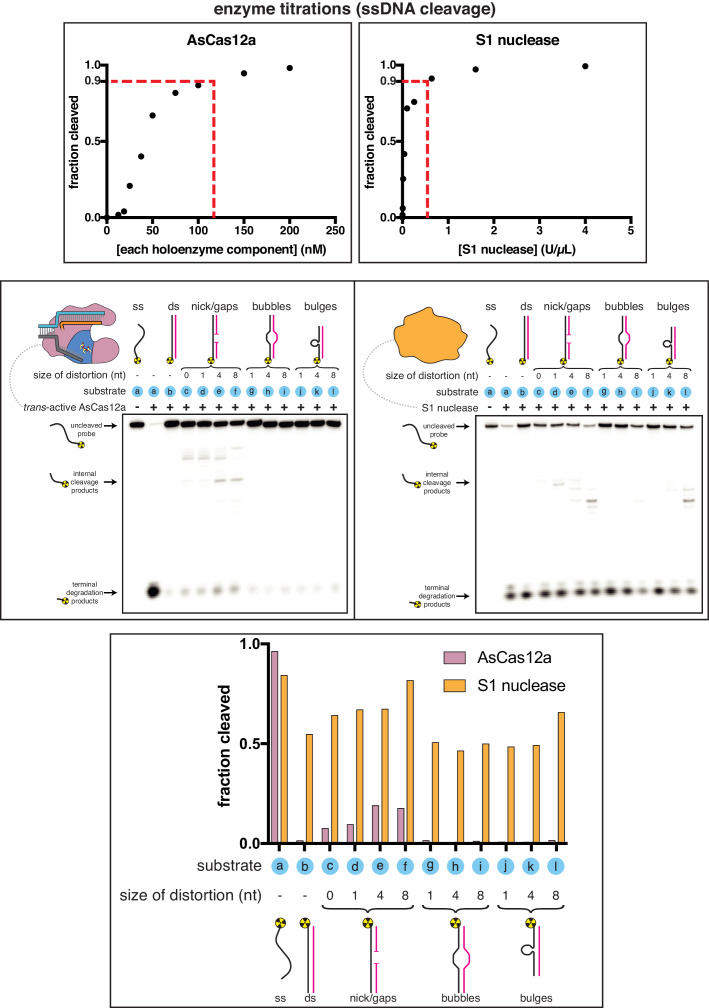
Top panel: Enzymes were first titrated in an activity assay with a radiolabeled ssDNA substrate to determine what concentration to use in substrate specificity assays. A ssDNA oligo (the same one shown in the other panels) was 5'-radiolabeled and incubated with varying concentrations of either AsCas12a/crRNA/pre-cleaved DNA activator (all components held equimolar at the indicated concentration) or S1 nuclease for 30 minutes at 30°C, followed by quenching. Products were resolved by denaturing PAGE and quantified from the phosphorimage. “U” on the x-axis of S1 nuclease refers to the units defined by the enzyme manufacturer. To achieve 90% cleavage of the ssDNA substrate in the given time course, 115 nM AsCas12a holoenzyme or 0.513 U/µL S1 nuclease was required. Middle panels: Phosphorimage of AsCas12a or S1 nuclease cleavage products, resolved by denaturing PAGE. Trans-active AsCas12a holoenzyme (115 nM of each component: protein, crRNA, pre-cleaved activator) or S1 nuclease (0.513 U/µL) was incubated with 1 nM of the indicated substrate for 2 hours at 30°C prior to quenching. Substrate (a) was a single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide with no homology to the crRNA. To generate substrates (b) through (l), substrate (a) was hybridized to a variety of unlabeled complementary DNA oligonucleotides. Substrate (c) contained a nick. Substrates (d), (e), and (f) contained gaps of 1, 4, and 8 nt, respectively. Substrates (g), (h), and (i) contained bubbles of 1, 4, and 8 nt, respectively. Substrates (j), (k), and (l) contained bulges of 1, 4, and 8 nt, respectively. Bottom panel: Quantifications of cleavage from phosphorimages. “Fraction cleaved” is defined as (sum of the volume of all bands below the uncleaved band)/(total volume in lane).