Figure 1. Glucose tolerance and β-cell morphometry in whole body WFS1–/– 129S6 mice.
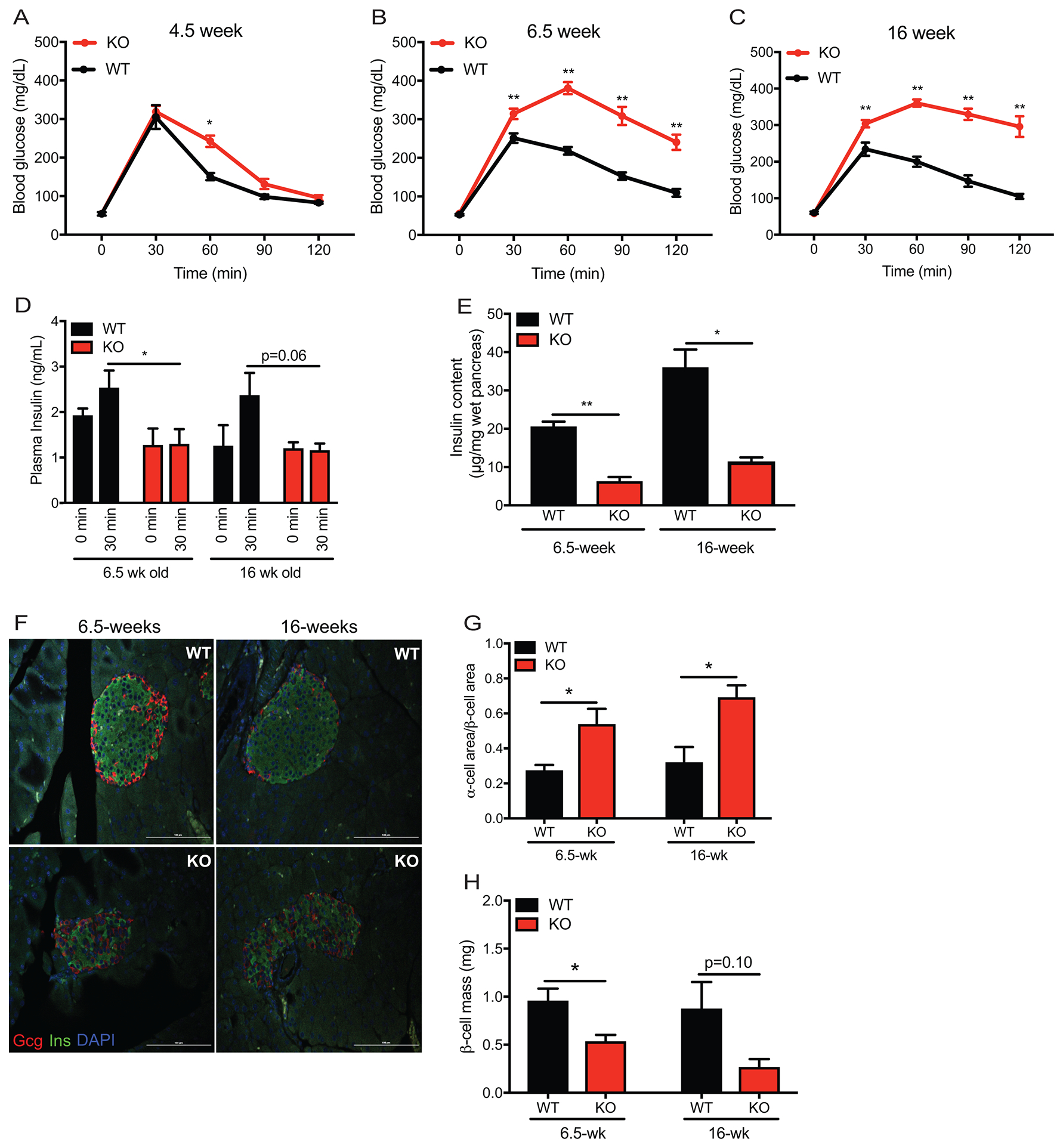
Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test of: (A) WFS1 KO (n=12) and WT control (n=6) mice at 4.5 weeks old, (B) WFS1 KO (n=21) and WT control (n = 19) mice at 6.5-weeks old and (C) WFS1 KO (n=7) and WT control (n=7) mice at 16-weeks old (*p<0.05, **p< 0.01). (D) Insulin levels 30 min after injection of glucose (2g/kg) in 6.5-week old and 16-week old mice (n=4 WFS1 KO mice at each age and n = 4 WT mice at each age, *p<0.05). (E) Total pancreatic insulin content in 6.5-week-old and 16-week-old mice (n = 4 WFS1 KO mice at each age and n = 4 WT mice at each age, *p<0.05, **p< 0.01) (F) Immunofluorescence of islets from control and WFS1 KO mice at 6.5 and 16-weeks of age. (G) Beta cell mass in WT and WFS1 KO mice at 6.5 and 16-weeks of age mice (n = 3 WFS1 KO mice at each age and n = 3 WT mice at each age). Black bars represent data from WT mice and red bars indicate data from Wfs1 KO mice. (H) Quantification of alpha cell area to beta cell area in WT and WFS1 KO mice at 6.5 and 16-weeks of age mice (n=3 Wfs1 KO mice and n = 3 WT mice at each age, *p<0.05). Data are represented as mean ± SEM from at least three mice per experiment. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired t-test.
