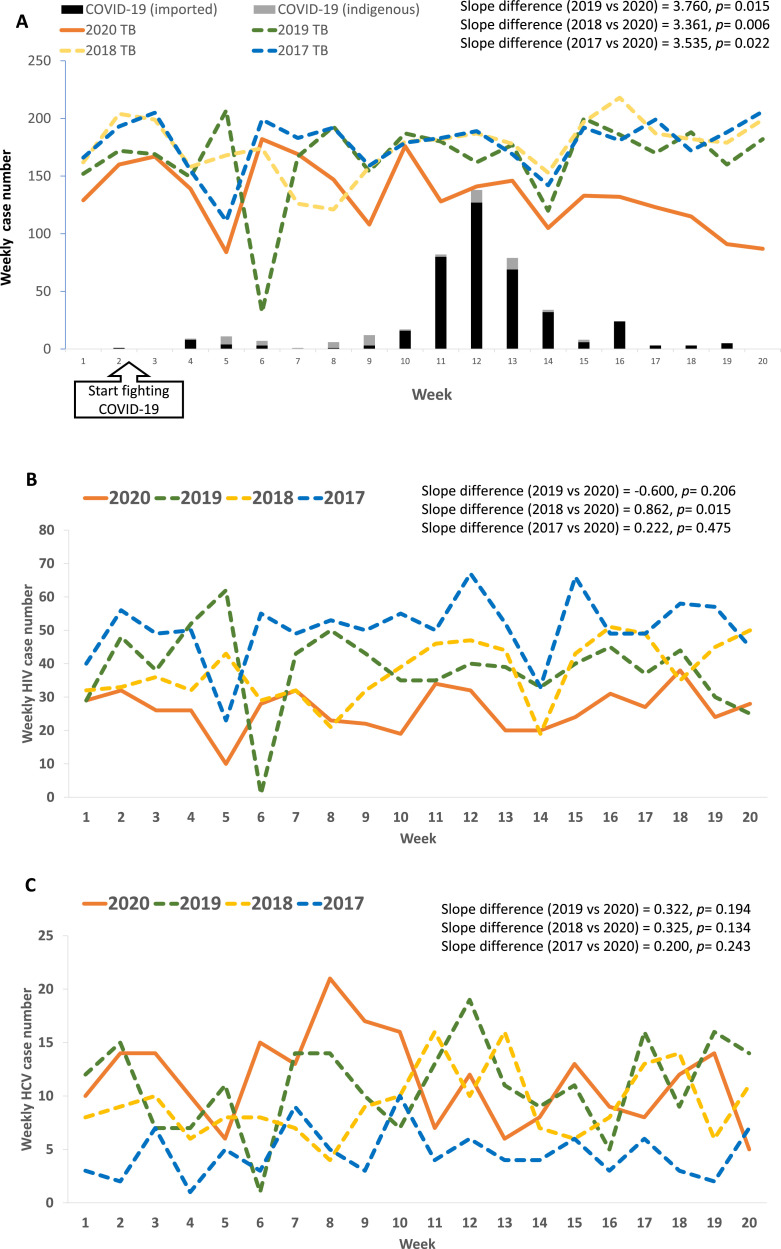
Fig. 1.
The trends of infectious events (TB, HIV, and HCV) during the first 20 calendar weeks of 2020 were compared to the events during the corresponding time period in 2017, 2018, and 2019. (A) The COVID-19 outbreak was successfully contained after initiating cotrol measures from the 2nd week, except for some imported cases peaked in the 12th week; the weekly TB cases showing slow decline of TB cases after fitiging COVID-19 outbreak, and significsnt trend difference of TB in 2020 (slope = −2.861) compared to 2019 (slope = 0.899), 2018 (slope = 1.500) and 2017 (slope = 0.674); (B) weekly HIV cases showing no significant trend difference of HIV in 2020 (slope = 0.000) compared to 2019 (slope = −0.600) and 2017 (slope = 0.222), except for 2018 (slope = 0.862); (C) weekly HCV cases showing no significant trend difference of HCV in 2020 (slope = −0.200) compared to 2019 (slope = 0.122), 2018 (slope = 0.125), and 2017 (slope = 0.000).