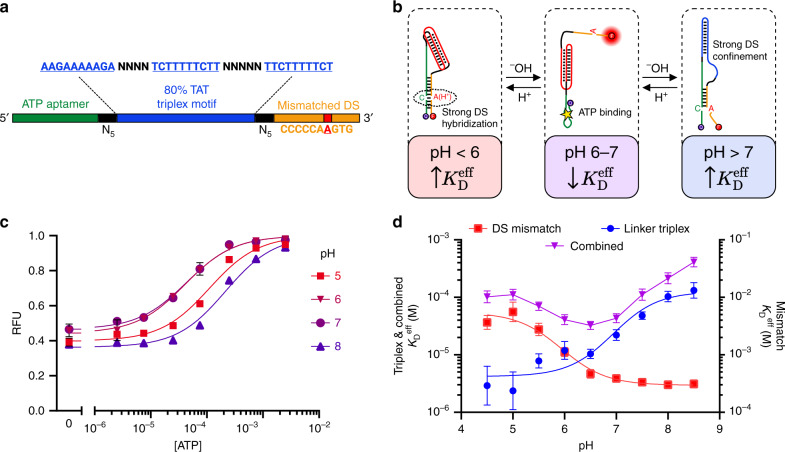
Fig. 4. PSD design for selective binding over a narrow pH window.
a We designed a construct that incorporated both an intramolecular triplex in the linker domain and an A–C mismatch in the displacement strand. b Complex pH dependence is achieved through a three-state system, where binding is inhibited by strong DS hybridization at low pH or strong DS confinement at high pH, with a small window between these extremes where binding affinity is high. c ATP binding curves for the combined construct show the highest affinity at pH 6–7, with lower affinity at both high and low pH. d The pH dependence of affinity for this construct ( plotted on left axis) reflects contributions from both the binding inhibition of the linker modification-based TAT80 construct at high pH (left axis) and the binding inhibition of the DS modification-based A–C mismatch construct at low pH (right axis). Data points and error bars in c show the means and standard deviations of n = 3 independent experiments. Data points and error bars in d show the best fit values and standard deviations extracted from Langmuir isotherm fits to binding curve data from n = 3 independent experiments (data given in Supplementary Fig. 7) using nonlinear least squares fitting. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.