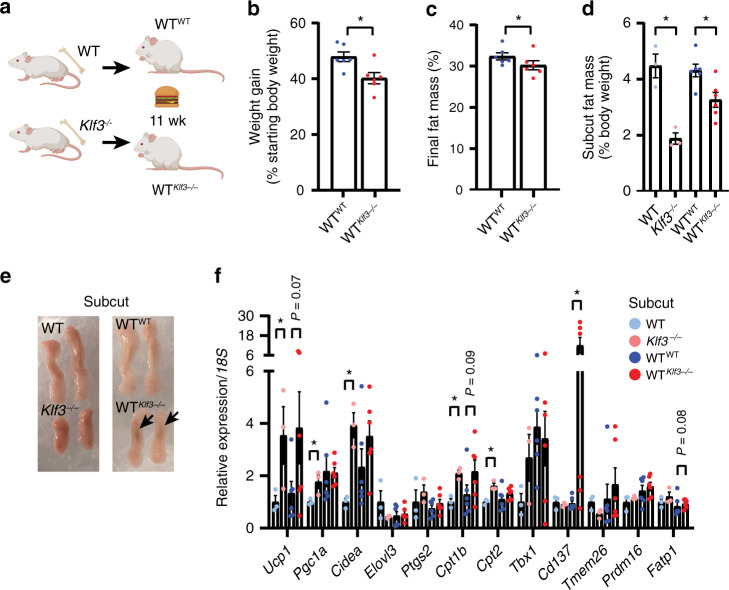
Fig. 3. Reduced weight gain in WT mice transplanted with Klf3−/− BM.
a WT mice were irradiated and transplanted with bone marrow from WT (WTWT) or Klf3−/− (WTKlf3−/−) donors then fed a high-fat, high-sugar (Western) diet for 11 weeks (wk) (cartoon created with BioRender.com). b Body weight was monitored throughout the Western diet study duration (weeks 2–13), and the total weight gained was calculated as a percentage of starting body weight at commencement of Western diet administration (n = 6 mice). c Fat mass composition (%) was assessed using EchoMRI after 11 weeks of Western diet (n = 6 mice). d Weights of subcut AT (relative to body weight) from WT, Klf3−/− (n = 3), WTWT and WTKlf3−/− (n = 6) mice fed a Western diet for 11 weeks. e Representative macroscopic images of subcut AT pads from mice of each condition, showing size and complexion. Arrows point to sites of enriched brown appearance. f mRNA levels of thermogenic genes in the subcut AT of WT, Klf3−/− (n = 3), WTWT and WTKlf3−/− (n = 6) mice were assessed by qPCR. Relative expression was normalised to levels of 18S rRNA and the mean WT value set to 1 for each target. For b–d and f, error bars represent means ± SEM and one-sided non-parametric Mann–Whitney U tests were performed where *P < 0.05. Source data are provided as a Source data file. See also Supplementary Figs. 4, 5.