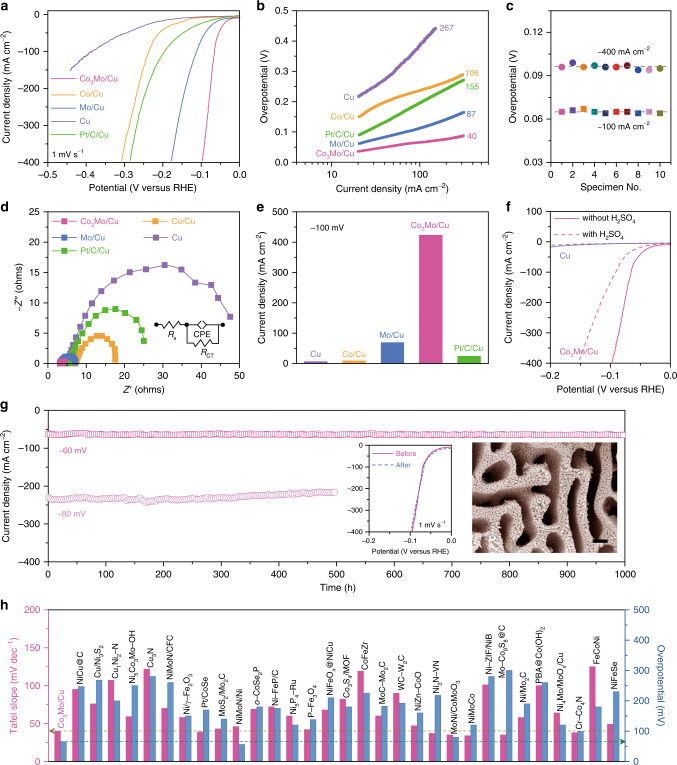
Fig. 3. Electrochemical characterization on HER properties.
a iR-corrected HER polarization curves for self-supported nanoporous Co3Mo/Cu, Co/Cu, Mo/Cu, and Cu electrodes, as well as commercially available Pt/C immobilized on nanoporous Cu (Pt/C/Cu) in 1 M KOH. Scan rate: 1 mV s−1. b Comparison of the Tafel plots of different electrocatalytic materials obtained from the HER polarization curves in panel (a). c Overpotentials at current densities of 100 and 400 mA cm−2 for ten nanoporous Co3Mo/Cu electrodes that are prepared by the same alloying/dealloying procedure. d EIS spectra of nanoporous Co3Mo/Cu, Co/Cu, Mo/Cu, and bare Cu electrodes and nanoporous Pt/C/Cu. e Comparison of current density at −100 mV for nanoporous Co3Mo/Cu electrode with the values of nanoporous Cu, Co/Cu, Mo/Cu electrodes, and nanoporous Pt/C/Cu. f iR-corrected HER polarization curves of nanoporous Co3Mo/Cu and bare Cu electrodes before and after H2SO4 treatment. g Long-term stability measurement of nanoporous Co3Mo/Cu electrode at the overpotentials of 60 and 80 mV for more than 1000 and 500 h, respectively. The negligible current fluctuation is due to the depletion/replenishment of electrolyte. Insets: SEM image after the durability measurement at 60 mV for 1000 h and polarization curves before and after the durability measurement. Scale bar: 300 nm. h Tafel slope and overpotential at 100 mA cm−2 of nanoporous Co3Mo/Cu electrode, comparing with the values of representative HER catalysts reported previously.