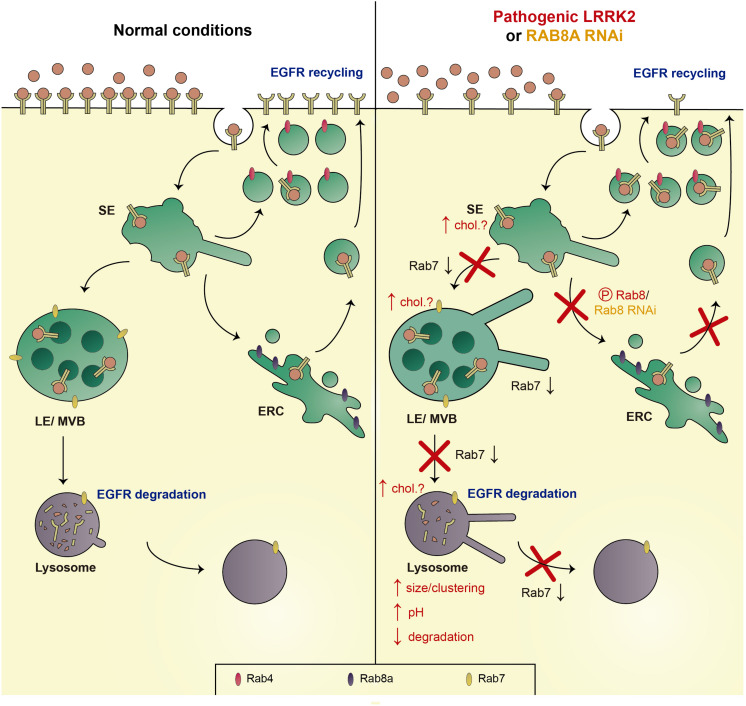
FIGURE 5.
Schematics of trafficking deficits mediated by pathogenic LRRK2 or knockdown of Rab8a. Left: Under normal conditions, the EGFR is either endocytosed and sorted to LE/MVB and the lysosome for degradation (EGFR degradation), or recycled back to the membrane via either a fast (Rab4-dependent) or a slow recycling pathway (Rab8a-dependent; EGFR recycling). Right: Pathogenic LRRK2 (via phosphorylation of Rab8a), or knockdown of Rab8a causes a decrease in active Rab7a, causing a deficit in trafficking from the SE to the LE/MVB, from the LE/MVB to the lysosome, as well as a deficit in lysosome reformation, associated with an increase in the size/clustering of lysosomes, an increase in lysosomal pH, and a decrease in lysosomal degradation. In addition, the LRRK2-mediated phosphorylation of Rab8a, or knockdown of Rab8a, causes a deficit in trafficking to/from the ERC, with a resultant accumulation of the EGFR in a Rab4-positive recycling compartment. Speculative alterations in cholesterol levels across the endocytic pathway may further contribute to the pathogenic LRRK2-mediated deficits (chol?). SE, sorting endosome; LE/MVB, late endosome/multivesicular body; and ERC, early recycling compartment.