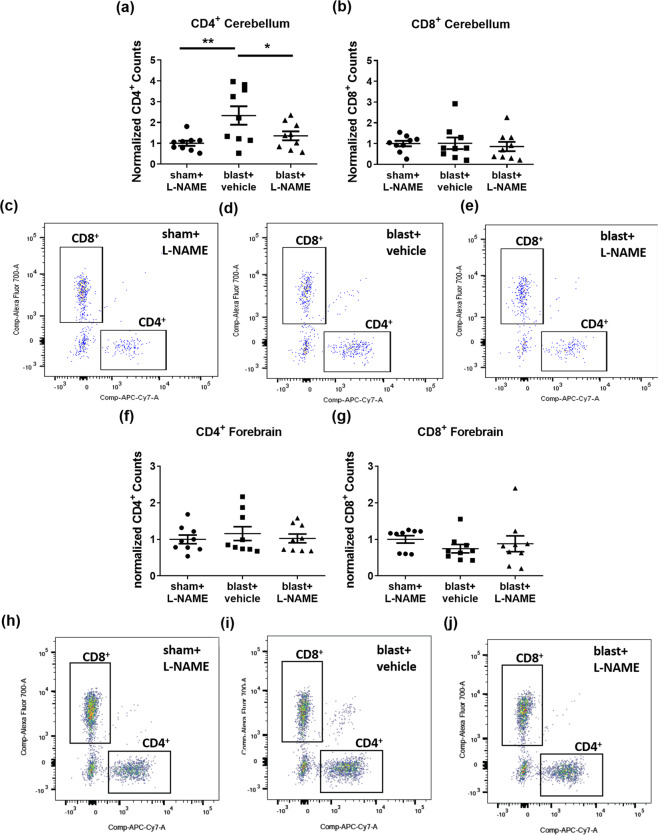
Figure 4.
Nitric oxide inhibition attenuates CD4+ T-cell infiltration in the cerebellum following repetitive blast. (a) Flow cytometry revealed that repetitive TBI significantly increased CD4+ counts in the cerebellum (**p ≤ 0.01), which was significantly attenuated by L-NAME administration (*p ≤ 0.05). (b) No differences were measured in cerebellar CD8+ counts after repetitive TBI (p > 0.05). (c) Scatter plots for cerebellum of shams, (d) blast vehicle-treated, and (e) blast L-NAME-treated mice. (f) No differences in CD4+ counts (p > 0.05), or (g) CD8+ counts were measured in forebrain after repetitive mTBI (p > 0.05). (h) Scatter plots for forebrain of shams, (i) blast + vehicle-treated, and (j) blast + L-NAME-treated mice. One-way ANOVA post-hoc Newman-Keuls. Values represent means ± SEM.