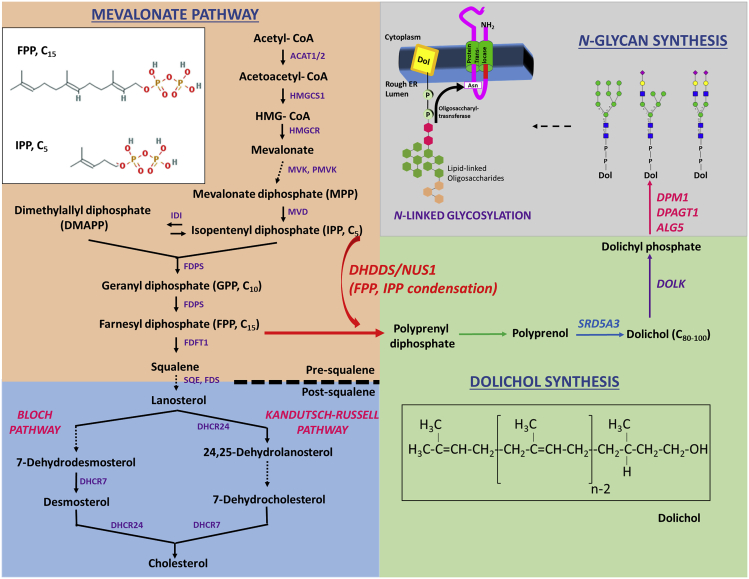
Figure 1.
Schematic Representation of the Mevalonate Pathway, Dolichol Synthesis, and the Requirement of Dolichyl Phosphate (Dol-P) for N-Linked Oligosaccharide Generation
Farnesyl diphosphate (FPP), an important pre-squalene intermediate of the mevalonate pathway, undergoes DHDDS/NUS1-catalyzed condensation with multiple isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) units to generate polyprenyl pyrophosphate (diphosphate), and ultimately the obligate glycan carrier, Dol-PP. Gene products involved in synthesis of dolichol and Dol-P-saccharide/oligosaccharide intermediates, and hence implicated in CDG-1 (Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation), have been represented. The enzymatic activity provided by DHDDS and NUS1 catalyzes the commitment step of dolichol synthesis; hence mutations in either DHDDS or NUS1 are hypothesized to block protein N-glycosylation, and are classified as CDG-I. Dolichol (structure in inset), is an acyclic isoprenoid consisting of 18–21 isoprene units.