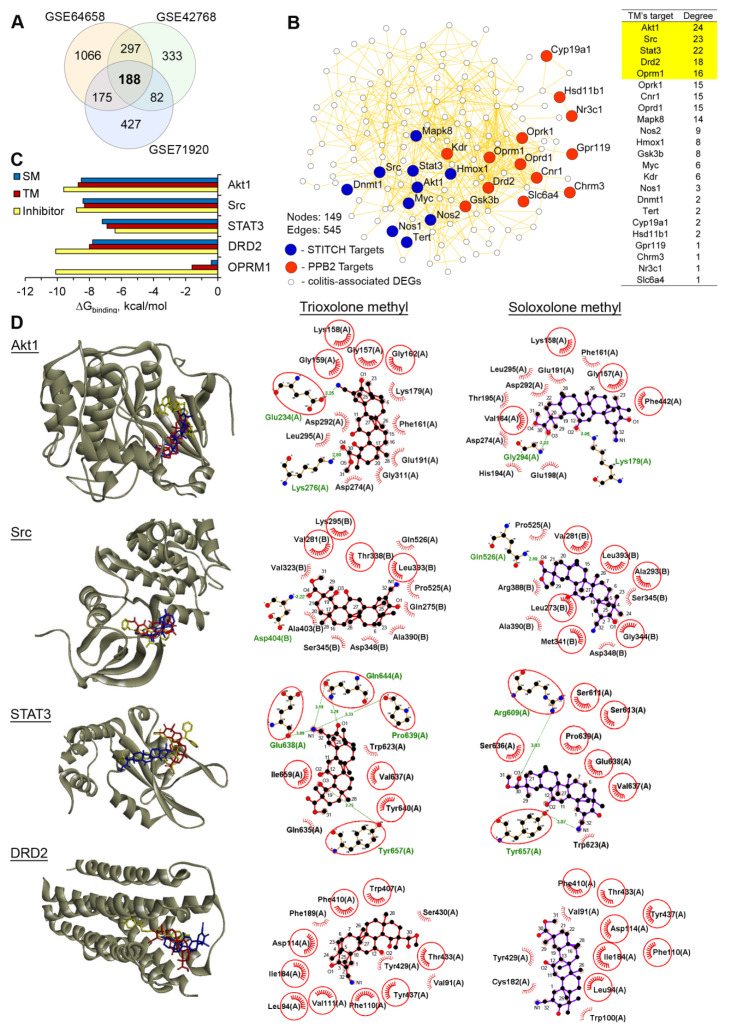
Figure 6.
AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (Akt1), tyrosine protein kinase Src, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) are probable primary targets of TM. (A) Venn diagram of the genes that were differentially expressed in the DSS-inflamed colon tissues in comparison with the healthy control (fold change > 1.5, p < 0.05) identified by the re-analysis of the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets. (B) The protein–protein interaction network containing the colitis-associated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and primary targets of TM, predicted by the Polypharmacology browser 2.0 tool (PB2) and the STITCH database, was reconstructed using the STRING database (confidence score > 0.7) in Cytoscape. The top 5 interconnected probable targets of SM are highlighted in yellow. (C) The binding energies of TM and the known inhibitors with the top 5 probable targets of TM that are the most associated with the colitis regulome. The binding energies were calculated by Autodock Vina. (D) The mode of binding of TM and SM to Akt1, Src, STAT3, and DRD2. Stereo presentation of the docked poses of TM and SM in the mentioned proteins, superimposed on the corresponding inhibitor-bound structures, created by BIOVIA Discovery Studio. Two-dimensional representations of the docked poses of TM and SM in Akt1, Src, STAT3, and DRD2, depicted by LigPlot+. The green lines and comb represent the hydrogen bonds and nonbonding contacts, respectively. Common amino acid residues, interacting with both TM/SM and the corresponding inhibitors, are highlighted in red circles.