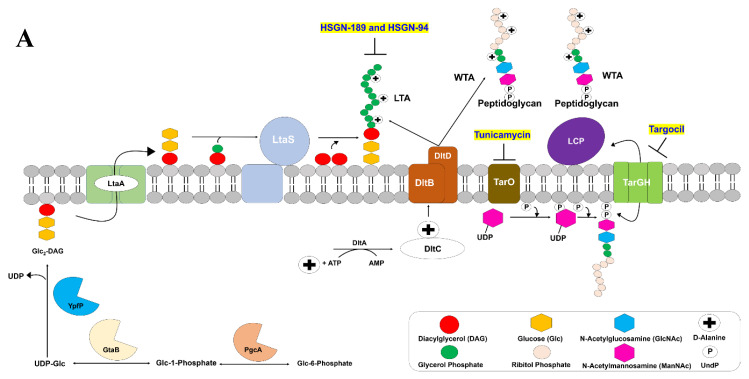
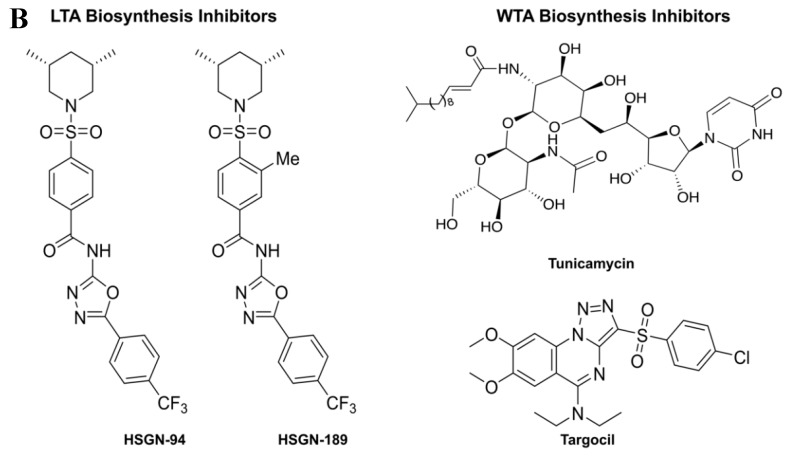
Figure 1.
(A) LTA biosynthesis occurs at the Gram-positive bacterial cell membrane. The α-phosphoglucomutase PgcA converts glucose-6-phosphate to glucose-1-phosphate, then uridyltransferase GtaB activates uridine triphosphate (UTP) to produce UDP-glc. Glc2-DAG is then produced from YpfP transfering two glucose molecules from UDP-Glc to DAG. Glc2-DAG is moved to the outer membrane by LtaA followed by LtaS adding glycerol phosphate to Glc2-DAG generate LTA. WTA biosynthesis begins in the cytoplasm where TarO plays a key role in generate the diphospho-ManNAc-GlcNAc-GroP polymer. TarGH then exports the WTA polymer to the cell membrane where the LytR-CpsA-Psr (LCP) proteins catalyze the covalent bond between the WTA and peptidoglycan. The d-alanine moieties are added by DltABC. (B) HSGN-94 and HSGN-189 inhibit LTA biosynthesis. Tunicamycin and Targocil inhibit WTA biosynthesis via inhibition of TarO and TarGH, respectively.